Dell PowerEdge XL 5133-4 Dell PowerEdge FTOS Command Line Reference Guide for - Page 17
Obtaining Help, Partial Keyword Example, Table 3-2., Short-cut Keys and their Actions
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge XL 5133-4 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 17 highlights
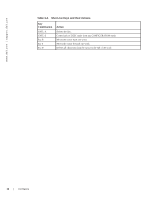
Obtaining Help As soon as you are in a command mode, there are several ways to access help. • To obtain a list of keywords at any command mode, do the following: - Enter a ? at the prompt or after a keyword. There must always be a space before the ?. • To obtain a list of keywords with a brief functional description, do the following: - Enter help at the prompt. • To obtain a list of available options, do the following: - Type a keyword followed by a space and a ? • Type a partial keyword followed by a ? - A display of keywords beginning with the partial keyword is listed. Figure 3-3 shows the results of entering ip ? at the prompt. Figure 3-3. Partial Keyword Example FTOS(conf)#ip ? igmp route telnet Internet Group Management Protocol Establish static routes Specify telnet options When entering commands, you can take advantage of the following time saving features: • The commands are not case sensitive. • You can enter partial (truncated) command keywords. For example, you can enter int tengig interface for the interface tengigabitethernet interface command. • Use the TAB key to complete keywords in commands. • Use the up arrow key to display the last enabled command. • Use either the Backspace key or the Delete key to erase the previous character. Use the left and right arrow keys to navigate left or right in the FTOS command line. Table 3-2 defines the key combinations valid at the FTOS command line. Table 3-2. Short-cut Keys and their Actions Key Combination CNTL-A CNTL-B CNTL-D CNTL-E CNTL-F CNTL-I CNTL-K CNTL-N CNTL-P CNTL-U CNTL-W Action Moves the cursor to the beginning of the command line. Moves the cursor back one character. Deletes character at cursor. Moves the cursor to the end of the line. Moves the cursor forward one character. Completes a keyword. Deletes all characters from the cursor to the end of the command line. Return to more recent commands in the history buffer after recalling commands with Ctrl-P or the up arrow key. Recalls commands, beginning with the last command. Deletes the line. Deletes the previous word. CLI Basics | 15