HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 113
Configuring port-based VLANs, Introduction to port-based VLAN, Port link type, PVID
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 113 highlights
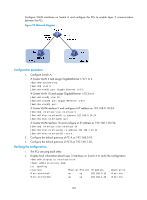
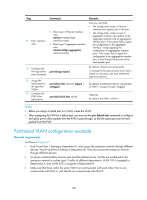
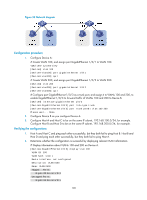
Configuring port-based VLANs Introduction to port-based VLAN Port-based VLANs group VLAN members by port. A port forwards traffic for a VLAN only after it is assigned to the VLAN. Port link type You can configure the link type of a port as access, trunk, or hybrid. The link types use the following VLAN tag handling methods: • An access port belongs to only one VLAN and sends traffic untagged. It is usually used to connect a terminal device unable to identify VLAN tagged-packets or when separating different VLAN members is unnecessary. • A trunk port can carry multiple VLANs to receive and send traffic for them. Except traffic from the port VLAN ID (PVID), traffic sent through a trunk port will be VLAN tagged. Usually, ports that connect network devices are configured as trunk ports. • Like a trunk port, a hybrid port can carry multiple VLANs to receive and send traffic for them. Unlike a trunk port, a hybrid port allows traffic of all VLANs to pass through VLAN untagged. You can configure a port connected to a network device or user terminal as a hybrid port. PVID By default, VLAN 1 is the PVID for all ports. You can configure the PVID for a port as required. When you configure the PVID on a port, use the following guidelines: • An access port can join only one VLAN. The VLAN to which the access port belongs is the PVID of the port. • A trunk or hybrid port can join multiple VLANs. You can configure a PVID for the port. • You can use a nonexistent VLAN as the PVID for a hybrid or trunk port but not for an access port. After you use the undo vlan command to remove the VLAN that an access port resides in, the PVID of the port changes to VLAN 1. The removal of the VLAN specified as the PVID of a trunk or hybrid port, however, does not affect the PVID setting on the port. When you configure a PVID, follow these guidelines: • Do not set the voice VLAN as the PVID of a port in automatic voice VLAN assignment mode. For information about voice VLAN, see "Configuring a voice VLAN." • HP recommends that you set the same PVID ID for local and remote ports. • Make sure that a port permits the traffic from its PVID to pass through. Otherwise, when the port receives frames tagged with the PVID or untagged frames, the port drops these frames. The following table shows how ports of different link types handle frames: Port type Actions (in the inbound direction) Untagged frame Tagged frame Actions (in the outbound direction) 104