HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 189
Configuring the customer-side port, Configuring the network-side port
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 189 highlights
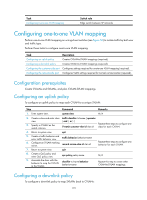
Step Command Remarks 1. Enter system view. system-view N/A 2. Create a class and enter class traffic classifier tcl-name [ operator view. { and | or } ] 3. Configure an SVLAN as the match criterion. if-match service-vlan-id vlan-id Repeat these steps to configure one class for each SVLAN. 4. Return to system view. quit 5. Create a traffic behavior and enter traffic behavior view. traffic behavior behavior-name 6. Configure a CVLAN marking action. remark customer-vlan-id vlan-id Repeat these steps to configure a behavior for each CVLAN. 7. Return to system view. quit 8. Create a QoS policy and enter QoS policy view. 9. Associate the class with the behavior to map the SVLAN to the CVLAN. qos policy policy-name classifier tcl-name behavior behavior-name N/A Repeat this step to create other CVLAN-to-SVLAN mappings. Configuring the customer-side port Step Command Remarks 1. Enter system view. system-view N/A 2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view. interface interface-type interface-number N/A 3. Configure the link type of the port. • Configure the port as a trunk port: port link-type trunk • Configure the port as a hybrid port: port link-type hybrid Use one of the commands. The default link type of an Ethernet port is access. • Assign the trunk port to VLANs: Use one of the commands. port trunk permit vlan { vlan-list | all } By default: 4. Assign the port to all CVLANs and SVLANs. • Assign the hybrid port to VLANs as a tagged member: • A trunk port is assigned only to VLAN 1. port hybrid vlan vlan-list • A hybrid port is an untagged tagged member of VLAN 1. 5. Enable basic QinQ. qinq enable By default, basic QinQ is disabled. 6. Apply the uplink policy to incoming traffic. qos apply policy policy-name inbound N/A 7. Apply the downlink policy to qos apply policy policy-name outgoing traffic. outbound N/A Configuring the network-side port 180