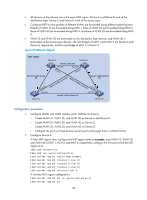
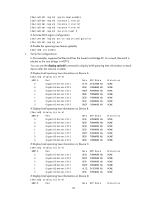
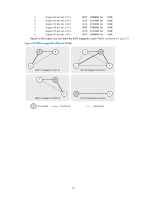
HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 95
Enabling loop guard, You cannot con edge port settings and loop guard
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 95 highlights
Enabling loop guard A device that keeps receiving BPDUs from the upstream device can maintain the state of the root port and blocked ports. However, link congestion or unidirectional link failures might cause these ports to fail to receive BPDUs from the upstream devices. The device will reselect the port roles: Those ports in forwarding state that failed to receive upstream BPDUs will become designated ports, and the blocked ports will transition to the forwarding state, resulting in loops in the switched network. The loop guard function can suppress the occurrence of such loops. The initial state of a loop guard-enabled port is discarding in every MSTI. When the port receives BPDUs, its state transitions normally. Otherwise, it stays in the discarding state to prevent temporary loops. Configure loop guard on the root port and alternate ports of a device. To enable loop guard: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 aggregate interface view. interface interface-type interface-number N/A 3. Enable the loop guard function for the ports. stp loop-protection Disabled by default. NOTE: • Do not enable loop guard on a port that connects user terminals. Otherwise, the port will stay in the discarding state in all MSTIs because it cannot receive BPDUs. • You cannot configure edge port settings and loop guard, or configure root guard and loop guard on a port at the same time. Enabling TC-BPDU guard When a switch receives topology change (TC) BPDUs (the BPDUs that notify devices of topology changes), the switch flushes its forwarding address entries. If someone forges TC-BPDUs to attack the switch, the switch will receive a large number of TC-BPDUs within a short time and be busy with forwarding address entry flushing. This affects network stability. With the TC-BPDU guard function, you can set the maximum number of immediate forwarding address entry flushes that the device can perform every a specified period of time (10 seconds). For TC-BPDUs received in excess of the limit, the device performs a forwarding address entry flush when the time period expires. This prevents frequent flushing of forwarding address entries. To enable TC-BPDU guard: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 86