HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 82
Configuring path costs of ports
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 82 highlights
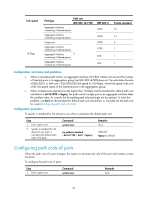
Configuring path costs of ports Path cost is a parameter related to the rate of a port. On a spanning tree device, a port can have different path costs in different MSTIs. Setting appropriate path costs allows VLAN traffic flows to be forwarded along different physical links, achieving VLAN-based load balancing. You can have the device automatically calculate the default path cost, or you can configure the path cost for ports. Specifying a standard for the device to use when it calculates the default path cost CAUTION: If you change the standard that the device uses to calculate the default path costs, you restore the path costs to the default. You can specify a standard for the device to use in automatic calculation for the default path cost. The device supports the following standards: • dot1d-1998-The device calculates the default path cost for ports based on IEEE 802.1d-1998. • dot1t-The device calculates the default path cost for ports based on IEEE 802.1t. • legacy-The device calculates the default path cost for ports based on a private standard. Table 13 shows the mappings between the link speed and the path cost. Table 13 Mappings between the link speed and the path cost Link speed 0 10 Mbps 100 Mbps 1000 Mbps Port type Path cost IEEE 802.1d-1998 N/A 65535 Single port Aggregate interface containing 2 Selected ports Aggregate interface 100 containing 3 Selected ports Aggregate interface containing 4 Selected ports Single port Aggregate interface containing 2 Selected ports Aggregate interface 19 containing 3 Selected ports Aggregate interface containing 4 Selected ports Single port Aggregate interface 4 containing 2 Selected ports IEEE 802.1t 200,000,000 2,000,000 Private standard 200,000 2000 1,000,000 1800 666,666 1600 500,000 200,000 100,000 1400 200 180 66,666 160 50,000 140 20,000 20 10,000 18 73