HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 39
Configuration classes, Reference port, LACP
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 39 highlights
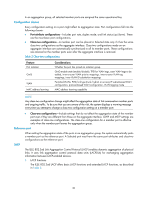
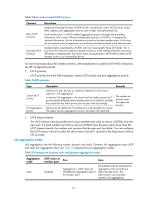
In an aggregation group, all selected member ports are assigned the same operational key. Configuration classes Every configuration setting on a port might affect its aggregation state. Port configurations fall into the following classes: • Port attribute configurations-Includes port rate, duplex mode, and link status (up/down). These are the most basic port configurations. • Class-two configurations-A member port can be placed in Selected state only if it has the same class-two configurations as the aggregate interface. Class-two configurations made on an aggregate interface are automatically synchronized to all its member ports. These configurations are retained on the member ports even after the aggregate interface is removed. Table 2 Class-two configurations Feature Port isolation QinQ VLAN MAC address learning Considerations Whether the port has joined an isolation group QinQ enable state (enable/disable), TPID for VLAN tags, outer VLAN tags to be added, inner-to-outer VLAN priority mappings, inner-to-outer VLAN tag mappings, inner VLAN ID substitution mappings Permitted VLANs, PVID, link type (trunk, hybrid, or access), IP subnet-based VLAN configuration, protocol-based VLAN configuration, VLAN tagging mode MAC address learning capability NOTE: Any class-two configuration change might affect the aggregation state of link aggregation member ports and ongoing traffic. To be sure that you are aware of the risk, the system displays a warning message every time you attempt to change a class-two configuration setting on a member port. • Class-one configurations-Include settings that do not affect the aggregation state of the member port even if they are different from those on the aggregate interface. GVRP and MSTP settings are examples of class-one configurations. The class-one configuration for a member port is effective only when the member port leaves the aggregation group. Reference port When setting the aggregation state of the ports in an aggregation group, the system automatically picks a member port as the reference port. A Selected port must have the same port attributes and class-two configurations as the reference port. LACP The IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) enables dynamic aggregation of physical links. It uses link aggregation control protocol data units (LACPDUs) for exchanging aggregation information between LACP-enabled devices. 1. LACP functions The IEEE 802.3ad LACP offers basic LACP functions and extended LACP functions, as described in Table 3. 30