HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 93
Configuration restrictions and guidelines, Configuration procedure, Configuring protection functions
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 93 highlights
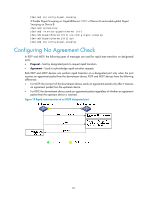
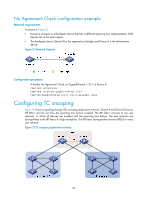
In the network, the IRF fabric transparently transmits the received BPDUs and does not participate in spanning tree calculations. When a topology change occurs to the IRF fabric or user networks, the IRF fabric may need a long time to learn the correct MAC address table entries and ARP entries, resulting in long network disruption. To avoid the network disruption, you can enable TC snooping on the IRF fabric. With TC snooping enabled, a device actively updates the MAC address table entries and ARP entries upon receiving TC-BPDUs, so that the device can normally forward the user traffic. For more information about MAC address table entries, see "Configuring the MAC address table." For more information about ARP, see Layer 3-IP Services Configuration Guide. Configuration restrictions and guidelines • TC snooping and STP are mutually exclusive. You must globally disable the spanning tree feature before enable TC snooping. • TC snooping does not take effect on the ports on which BPDU tunneling is enabled for spanning tree protocols. For more information about BPDU tunneling, see "Configuring BPDU tunneling." Configuration procedure To configure TC snooping: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Globally disable the spanning tree feature. 3. Enable TC snooping. Command system-view undo stp enable stp tc-snooping Description N/A By default, the spanning tree feature is disabled globally. Disabled by default. Configuring protection functions A spanning tree device supports the following protection functions: • BPDU guard • Root guard • Loop guard • TC-BPDU guard Configuration prerequisites Correctly configure the spanning tree feature on the device. Enabling BPDU guard For access layer devices, the access ports can directly connect to the user terminals (such as PCs) or file servers. The access ports are configured as edge ports to allow rapid transition. When these ports receive configuration BPDUs, the system automatically sets the ports as non-edge ports and starts a new spanning tree calculation process. This causes a change of network topology. Under normal conditions, these ports should not receive configuration BPDUs. However, if someone forges configuration BPDUs maliciously to attack the devices, the network will become unstable. 84