HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 121
Dynamic MAC-based VLAN, Configuration restrictions and guidelines, Configuration procedure
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 121 highlights
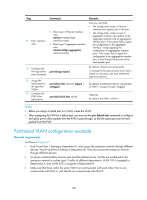
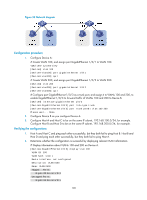
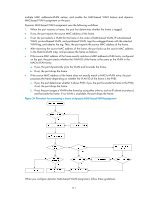
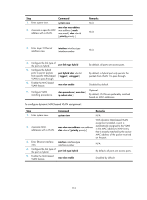
• When a port is assigned to the corresponding VLAN in a MAC address-to-VLAN entry, but has not been assigned to the VLAN by using the port hybrid vlan command, the port sends packets from the VLAN with VLAN tags removed. • If you configure both static and dynamic MAC-based VLAN assignment on the same port, dynamic MAC-based VLAN assignment applies. • A port forwards frames matching MAC-to-VLAN entries according to the 802.1p priorities of the MAC-based VLANs. Dynamic MAC-based VLAN You can use dynamic MAC-based VLAN with access authentication (such as 802.1X authentication based on MAC addresses) to implement secure, flexible terminal access. After configuring dynamic MAC-based VLAN on the device, you must configure the username-to-VLAN entries on the access authentication server. When a user passes authentication of the access authentication server, the device obtains VLAN information from the server, generates a MAC address-to-VLAN entry by using the source MAC address of the user packet and the VLAN information, and assigns the port to the MAC-based VLAN. When the user goes offline, the device automatically deletes the MAC address-to-VLAN entry, and removes the port from the MAC-based VLAN. For more information about 802.1X and MAC authentication, see Security Configuration Guide. Configuration restrictions and guidelines When you configure a MAC-based VLAN, follow these guidelines: • MAC-based VLANs are available only on hybrid ports. • With dynamic MAC-based VLAN assignment enabled, packets are delivered to the CPU for processing. The packet processing mode has the highest priority and overrides the configuration of MAC learning limit and disabling of MAC address learning. When dynamic MAC-based VLAN assignment is enabled, do not configure the MAC learning limit or disable MAC address learning. • Do not use dynamic MAC-based VLAN assignment together with 802.X and MAC authentication. • In dynamic MAC-based VLAN assignment, the port that receives a packet with an unknown source MAC address can be successfully assigned to the matched VLAN only when the matched VLAN is a static VLAN. • The MAC-based VLAN feature is mainly configured on the downlink ports of the user access devices. Do not enable this function together with link aggregation. • With MSTP enabled, if a port is blocked in the MST instance (MSTI) of the target MAC-based VLAN, the port drops the received packets, instead of delivering them to the CPU. As a result, the receiving port will not be dynamically assigned to the corresponding VLAN. Do not configure dynamic MAC-based VLAN assignment together with MSTP, because the former is mainly configured on the access side. • When PVST is enabled, if the VLAN to which a port is to be assigned is not allowed by the port, the port is blocked. In this case, the port drops received packets instead of delivering them to the CPU, failing to complete dynamic MAC-based VLAN assignment. Do not configure dynamic MAC-based VLAN assignment together with PVST, because the former is mainly configured on the access side. Configuration procedure To configure static MAC-based VLAN assignment: 112