HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 91
Configuration prerequisites, To con No Agreement Check
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 91 highlights
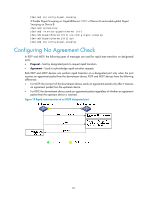
Figure 20 Rapid state transition of an RSTP designated port If the upstream device is a third-party device, the rapid state transition implementation might be limited. For example, when the upstream device uses a rapid transition mechanism similar to that of RSTP, and the downstream device adopts MSTP and does not operate in RSTP mode, the root port on the downstream device receives no agreement packet from the upstream device and sends no agreement packets to the upstream device. As a result, the designated port of the upstream device fails to transit rapidly, and can only change to the forwarding state after a period twice the Forward Delay. You can enable the No Agreement Check feature on the downstream device's port to enable the designated port of the upstream device to transit its state rapidly. Configuration prerequisites Before you configure the No Agreement Check function, complete the following tasks: • Connect a device to a third-party upstream device that supports spanning tree protocols via a point-to-point link. • Configure the same region name, revision level and VLAN-to-instance mappings on the two devices, assigning them to the same region. Configuration procedure To make the No Agreement Check feature take effect, enable it on the root port. To configure No Agreement Check: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 interface interface-type interface-number aggregate interface view. N/A 3. Enable No Agreement Check. stp no-agreement-check Disabled by default. 82