HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 186
VLAN mapping implementations, One-to-one VLAN mapping
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 186 highlights
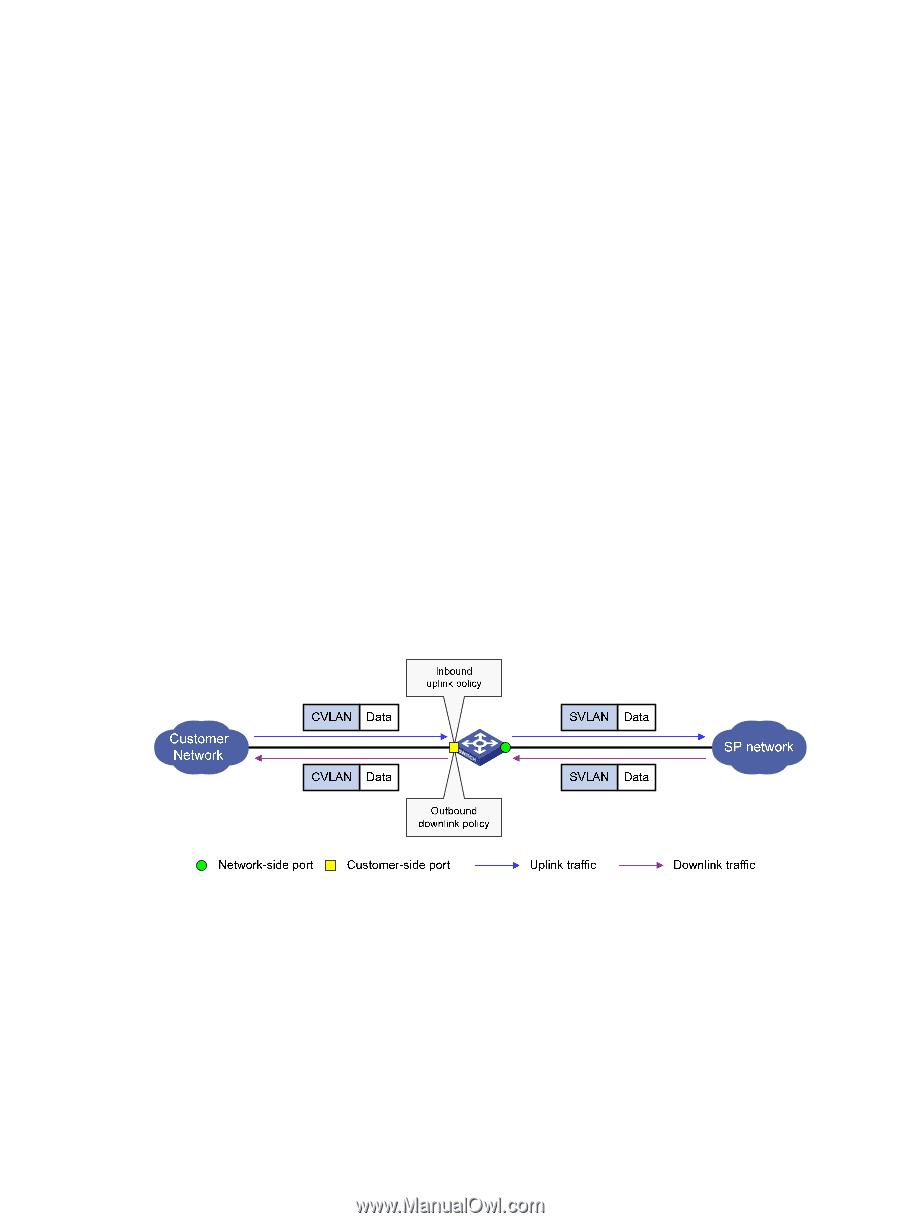
• Uplink traffic-Traffic transmitted from the customer network to the service provider network. • Downlink traffic-Traffic transmitted from the service provider network to the customer network. • Network-side port-A port connected to or closer to the service provider network. • Customer-side port-A port connected to or closer to the customer network. • Uplink policy-A QoS policy that defines VLAN mapping rules for uplink traffic. • Downlink policy-A QoS policy that defines VLAN mapping rules for downlink traffic. • Customer VLANs (CVLANs)-VLANs assigned for customers. • Service provider VLANs (SVLANs)-VLANs assigned for transmitting traffic across the service provider network. For more information about QoS policies, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide. VLAN mapping implementations This section describes how VLAN mapping is implemented on your device. One-to-one VLAN mapping Implement one-to-one VLAN mapping on the customer-side port through the following configurations, as shown in Figure 59: • Apply an uplink policy to the incoming traffic, mapping each CVLAN ID to a unique SVLAN ID. When a packet arrives, the switch replaces its CVLAN ID with the matching SVLAN ID. • Apply a downlink policy to the outgoing traffic, mapping each SVLAN ID back to its corresponding CVLAN ID. When forwarding a packet out of the port, the switch replaces its SVLAN ID with the matching CVLAN ID. Figure 59 One-to-one VLAN mapping implementation One-to-two VLAN mapping Implement one-to-two VLAN mapping through the following configurations, as shown in Figure 60: • Apply an uplink policy to the incoming traffic on the customer-side port to tag the incoming packets from a certain CVLAN with an outer SVLAN tag. • Configure the customer-side port as a hybrid port, and assign the port to SVLANs as an untagged member. When the port forwards the packets from these SVLANs, it removes their SVLAN tag. 177