HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 165
Implementations of QinQ, Modifying the TPID in a VLAN tag, Modify the inner VLAN ID.
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 165 highlights
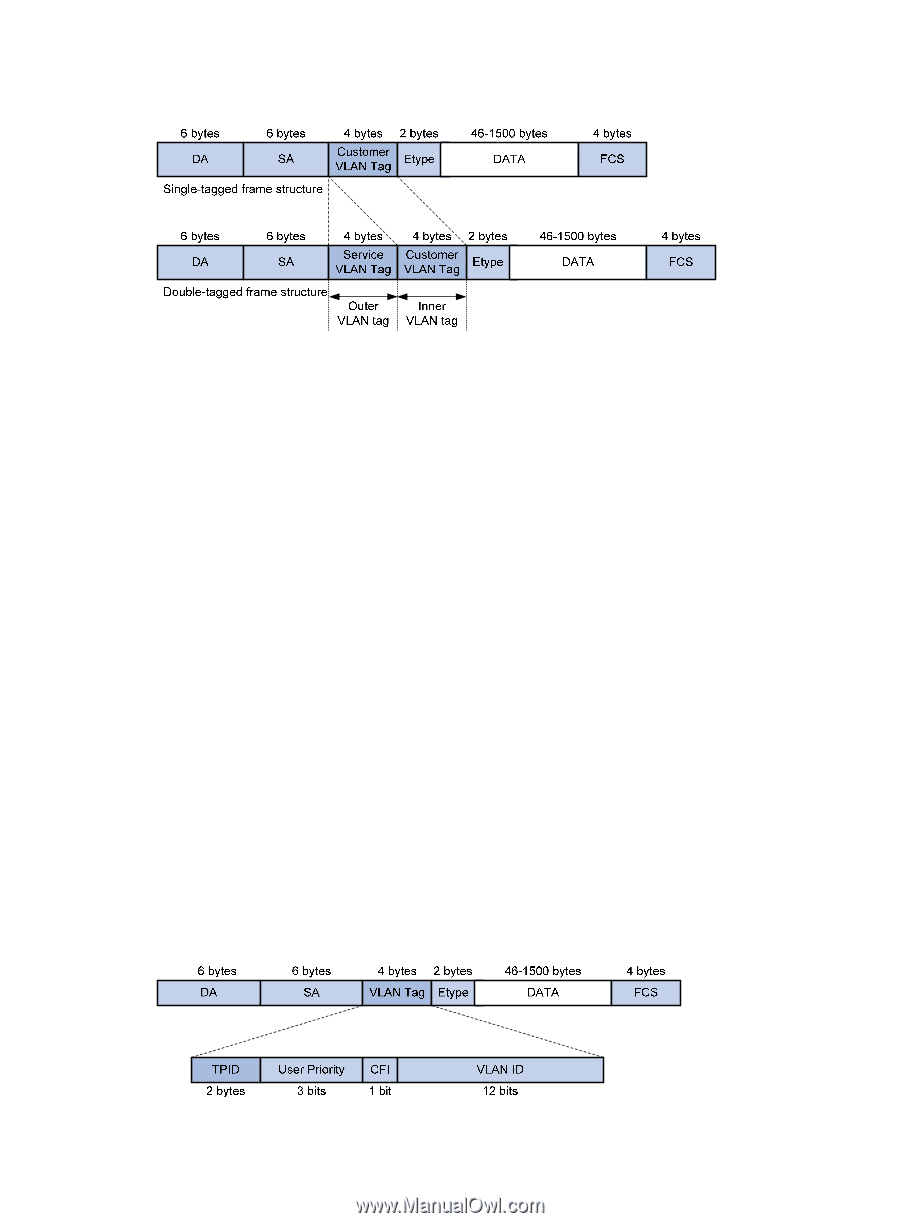
Figure 50 Single-tagged Ethernet frame header and double-tagged Ethernet frame header On the other devices in the network, the interfaces may be configured with the MTU of 1500 bytes. The size of an outer VLAN tag is 4 bytes. HP recommends that you increase the MTU of each interface on the service provider network to at least 1504 bytes. Implementations of QinQ HP provides the following QinQ implementations: basic QinQ and selective QinQ. • Basic QinQ Basic QinQ enables a port to tag any incoming frames with its port VLAN ID (PVID) tag, regardless of whether they have been tagged or not. If an incoming frame has been tagged, it becomes a double-tagged frame. If not, it becomes a frame tagged with the PVID tag. • Selective QinQ Selective QinQ is more flexible than basic QinQ. In addition to all the functions of basic QinQ, selective QinQ enables a port to perform the following per-CVLAN actions for incoming frames: { Tag frames from different CVLANs with different SVLAN tags. { Mark the outer VLAN 802.1p priority based on the existing inner VLAN 802.1p priority. { Modify the inner VLAN ID. Besides being able to separate the service provider network from the customer networks, selective QinQ provides abundant service features and enables more flexible networking. Modifying the TPID in a VLAN tag A VLAN tag uses the tag protocol identifier (TPID) field to identify the protocol type of the tag. The default value of this field, as defined in IEEE 802.1Q, is 0x8100. Figure 51 shows the 802.1Q-defined tag structure of an Ethernet frame. Figure 51 VLAN tag structure of an Ethernet frame 156