HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 203
Configuring LLDP, Overview, Background, Basic concepts, LLDPDU formats
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 203 highlights
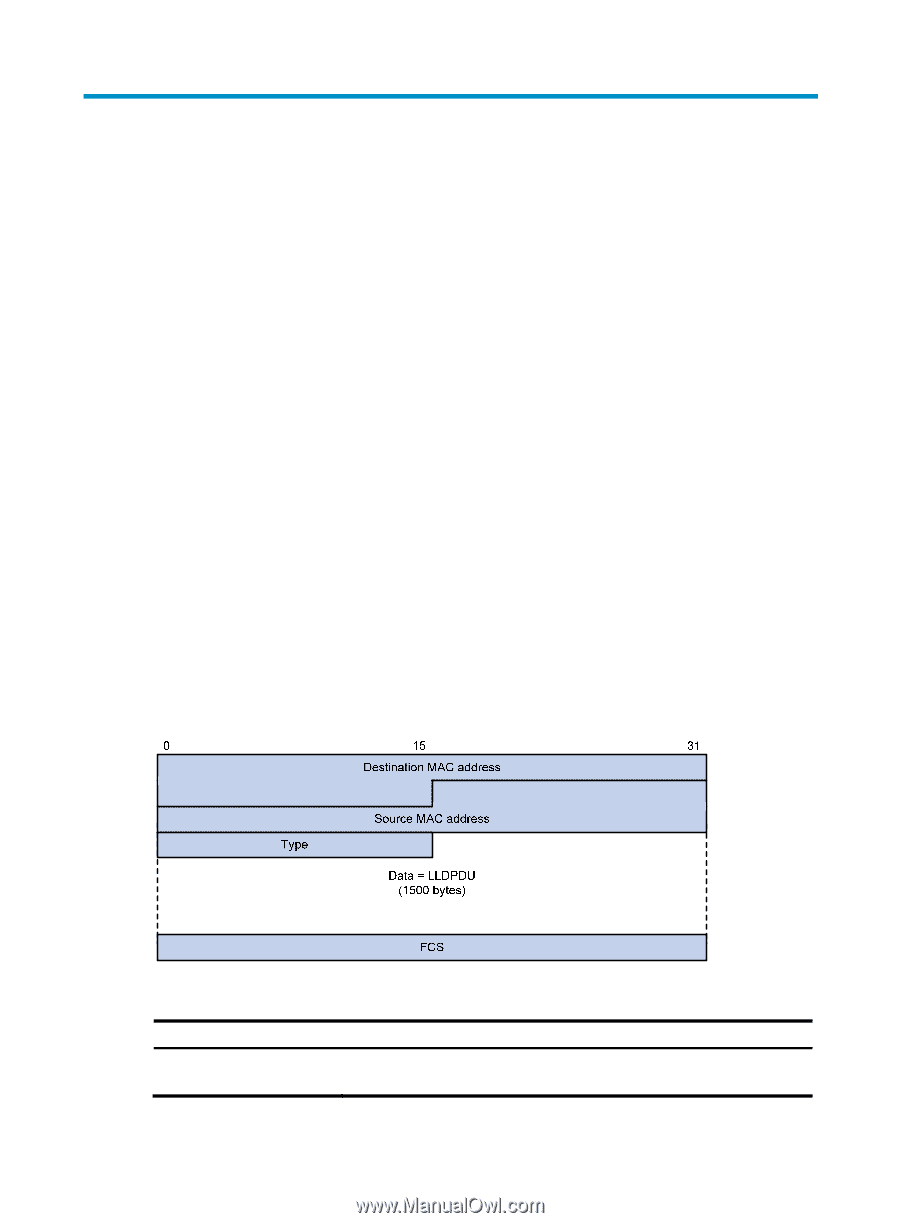
Configuring LLDP Overview Background In a heterogeneous network, a standard configuration exchange platform ensures that different types of network devices from different vendors can discover one another and exchange configuration for the sake of interoperability and management. The IETF drafted the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) in IEEE 802.1AB. The protocol operates on the data link layer to exchange device information between directly connected devices. With LLDP, a device sends local device information (including its major functions, management IP address, device ID, and port ID) as TLV (type, length, and value) triplets in LLDP Data Units (LLDPDUs) to the directly connected devices. At the same time, the device stores the device information received in LLDPDUs sent from the LLDP neighbors in a standard management information base (MIB). For more information about MIBs, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide. LLDP enables a network management system to quickly detect and identify Layer 2 network topology changes. Basic concepts LLDPDU formats LLDP sends device information in LLDPDUs. LLDPDUs are encapsulated in Ethernet II or Subnetwork Access Protocol (SNAP) frames. 1. Ethernet II-encapsulated LLDPDU format Figure 64 Ethernet II-encapsulated LLDPDU format Table 21 Fields in an Ethernet II-encapsulated LLDPDU Field Destination MAC address Description MAC address to which the LLDPDU is advertised. It is fixed to 0x0180-C200-000E, a multicast MAC address. 194