HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 207
Management address, How LLDP works, Operating modes of LLDP, Transmitting LLDPDUs - firmware
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 207 highlights
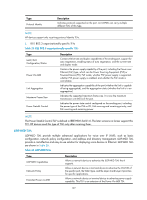
Type Hardware Revision Firmware Revision Software Revision Serial Number Manufacturer Name Model Name Asset ID Location Identification Description Allows a terminal device to advertise its hardware version. Allows a terminal device to advertise its firmware version. Allows a terminal device to advertise its software version. Allows a terminal device to advertise its serial number. Allows a terminal device to advertise its vendor name. Allows a terminal device to advertise its model name. Allows a terminal device to advertise its asset ID. The typical case is that the user specifies the asset ID for the endpoint to facilitate directory management and asset tracking. Allows a network device to advertise the appropriate location identifier information for a terminal device to use in the context of location-based applications. Management address The network management system uses the management address of a device to identify and manage the device for topology maintenance and network management. The management address TLV encapsulates the management address. How LLDP works Operating modes of LLDP LLDP can operate in one of the following modes: • TxRx mode-A port in this mode sends and receives LLDPDUs. • Tx mode-A port in this mode only sends LLDPDUs. • Rx mode-A port in this mode only receives LLDPDUs. • Disable mode-A port in this mode does not send or receive LLDPDUs. Each time the LLDP operating mode of a port changes, its LLDP protocol state machine re-initializes. A re-initialization delay, which is user configurable, prevents LLDP from being initialized too frequently at times of frequent changes to the operating mode. With this delay configured, before a port can initialize LLDP, it must wait for the specified interval after the LLDP operating mode changes. Transmitting LLDPDUs An LLDP-enabled port operating in TxRx mode or Tx mode sends LLDPDUs to its directly connected devices both periodically and when the local configuration changes. To prevent LLDPDUs from overwhelming the network during times of frequent changes to local device information, an interval is introduced between two successive LLDPDUs. This interval is shortened to 1 second in either of the following cases: • A new neighbor is discovered. A new LLDPDU is received and carries device information new to the local device. • The LLDP operating mode of the port changes from Disable or Rx to TxRx or Tx. This is the fast sending mechanism of LLDP. With this mechanism, a specific number of LLDPDUs are sent successively at 1-second intervals, to help LLDP neighbors discover the local device as soon as possible. Then, the normal LLDPDU transmit interval resumes. 198