HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 25
Configuring a null interface, Introduction to the null interface, Configuration procedure
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 25 highlights
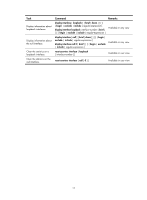
Step 4. Shut down the loopback interface. Command shutdown 5. Restore the default settings for the loopback interface. default Remarks Optional By default, a loopback interface is up. Optional NOTE: You can configure settings such as IP addresses and IP routes on loopback interfaces. For more information, see Layer 3-IP Services Configuration Guide and Layer 3-IP Routing Configuration Guide. Configuring a null interface Introduction to the null interface A null interface is a completely software-based logical interface, and is always up. However, you cannot use it to forward data packets or configure an IP address or link-layer protocol on it. With a null interface specified as the next hop of a static route to a specific network segment, any packets routed to the network segment are dropped. The null interface provides a simpler way to filter packets than ACL. You can filter uninteresting traffic by transmitting it to a null interface instead of applying an ACL. For example, by executing the ip route-static 92.101.0.0 255.255.0.0 null 0 command (which configures a static route that leads to null interface 0), you can have all the packets destined to the network segment 92.101.0.0/16 discarded. Only one null interface, Null 0, is supported on your switch. You cannot remove or create a null interface. Configuration procedure Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter null interface view. Command system-view interface null 0 3. Set the interface description. 4. Restore the default settings for the null interface. description text default Remarks N/A The Null 0 interface is the default null interface on your switch. It cannot be manually created or removed. Optional By default, the description of a null interface is interface name Interface. Optional Displaying and maintaining loopback and null interfaces 16