HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 14
Configuring link change suppression on an Ethernet interface
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
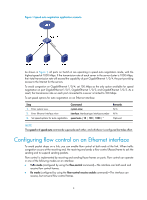
As shown in Figure 2, when both Port A and Port B forward packets at the rate of 1000 Mbps, Port C is congested. To avoid packet loss, enable flow control on Port A and Port B. Figure 2 Flow control on ports Configure flow control in TxRx mode on Port B and flow control in Rx mode on Port A: • When congestion occurs on Port C, Switch B buffers frames. When the amount of buffered frames exceeds a certain value, Switch B sends a common Pause frame out of Port B to ask Port A to suspend sending packets. This Pause frame also tells Port A for how long it is expected to pause. • Upon receiving the common Pause frame from Port B, Port A suspends sending packets to Port B for a period. • If congestion persists, Port B keeps sending common Pause frames to Port A until the congestion condition is removed. To handle unidirectional traffic congestion on a link, configure the flow-control receive enable command at one end, and the flow-control command at the other. To enable both ends of the link to handle traffic congestion, configure the flow-control command at both ends. To enable flow control on an Ethernet interface: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter Ethernet interface view. 3. Enable flow control. Command system-view interface interface-type interface-number • Enable TxRx flow control: flow-control • Enable Rx flow control: flow-control receive enable Remarks N/A N/A Use either command. By default, Rx flow control is disabled on an Ethernet interface. Configuring link change suppression on an Ethernet interface An Ethernet interface has two physical link states: up and down. Each time the physical link of an interface goes up or comes down, the physical layer reports the change to the upper layers, and the upper layers handle the change, resulting in increased overhead. To prevent physical link flapping from affecting system performance, configure link change suppression to delay the reporting of physical link state changes. When the delay expires, the interface reports any detected change. Link change suppression does not suppress administrative up or down events. When you shut down or bring up an interface by using the shutdown or undo shutdown command, the interface reports the event to the upper layers immediately. Link-down event suppression enables an interface to suppress link-down events and start a delay timer each time the physical link goes down. During this delay, the interface does not report the link-down 5