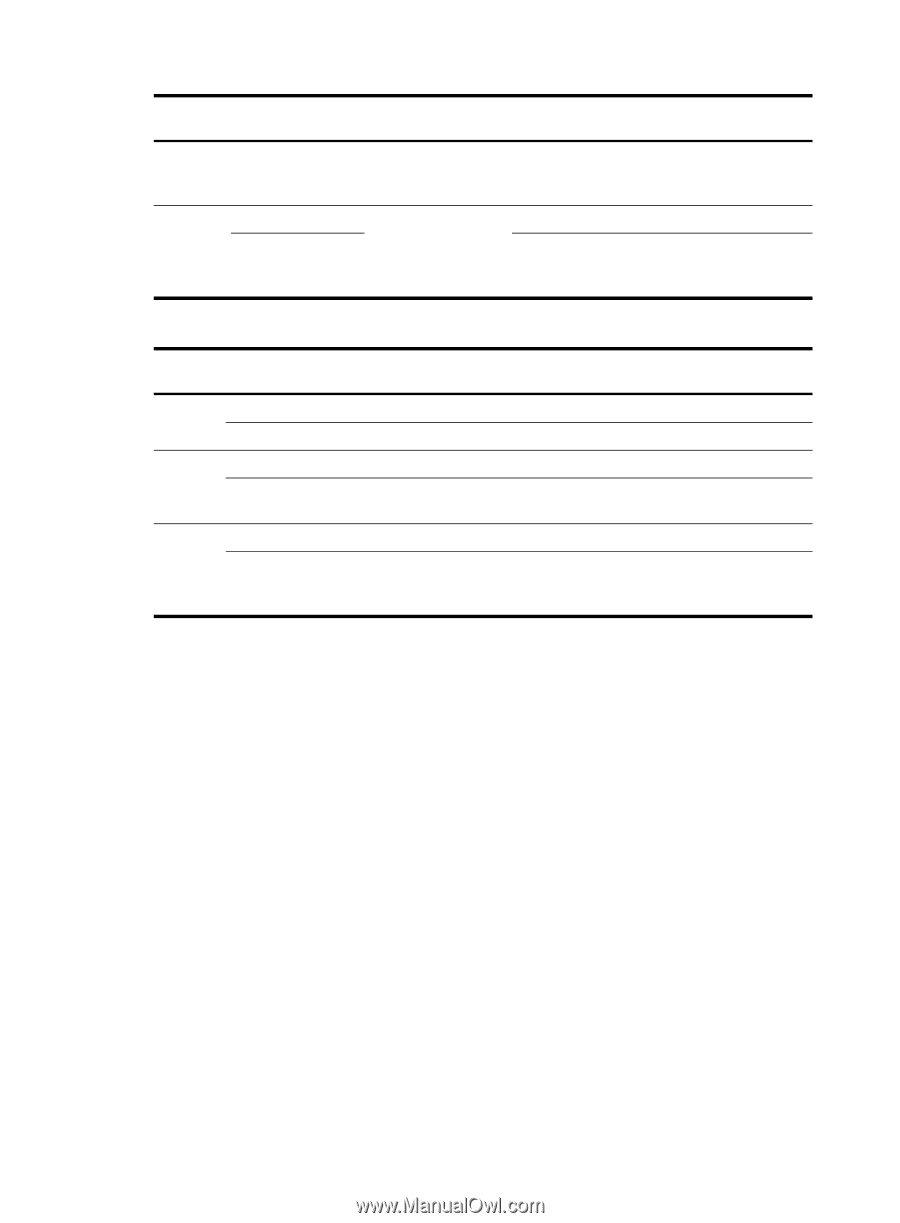
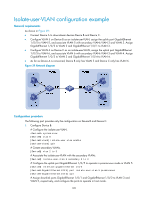
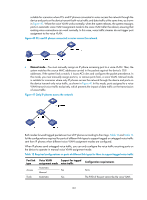
HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 2 - LAN Switching Co - Page 142
Security mode and normal mode of voice VLANs, Port link, Voice VLAN, assignment mode
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 142 highlights
Port link type Hybrid Voice VLAN Support for tagged assignment mode voice traffic Manual Automatic Yes Manual Configuration requirements The PVID of the port cannot be the voice VLAN. Configure the port to permit packets of the voice VLAN to pass through. The PVID of the port cannot be the voice VLAN. The PVID of the port cannot be the voice VLAN. Configure the port to permit packets of the voice VLAN to pass through tagged. Table 16 Required configurations on ports of different link types for them to support tagged voice traffic Port link type Voice VLAN assignment mode Support for untagged voice traffic Configuration requirements Automatic No Access Manual Yes N/A Configure the PVID of the port as the voice VLAN. Automatic No Trunk Manual Yes N/A Configure the PVID of the port as the voice VLAN and assign the port to the voice VLAN. Automatic No N/A Hybrid Manual Yes Configure the PVID of the port as the voice VLAN and configure the port to permit packets of the voice VLAN to pass through untagged. When you configure the voice VLAN assignment modes, follow these guidelines: • If an IP phone sends tagged voice traffic and its accessing port is configured with 802.1X authentication and any of the guest VLAN, Auth-Fail VLAN, and critical VLAN features, assign different VLAN IDs to the voice VLAN, PVID of the connecting port, and 802.1X guest, Auth-Fail, or critical VLAN. • If an IP phone sends untagged voice traffic, to implement the voice VLAN feature, you must configure the PVID of the IP phone's accessing port as the voice VLAN. As a result, you cannot implement 802.1X authentication. • The PVID is VLAN 1 for all ports by default. You can configure the PVID of a port and assign a port to certain VLANs by using commands. For more information, see "Configuring VLANs." • Use the display interface command to display the PVID of a port and the VLANs to which the port is assigned. Security mode and normal mode of voice VLANs Depending on their inbound packet filtering mechanisms, voice VLAN-enabled ports operate in the following modes: • Normal mode-Voice VLAN-enabled ports receive packets that carry the voice VLAN tag, and forward packets in the voice VLAN without comparing their source MAC addresses against the OUI addresses configured for the device. If the PVID of the port is the voice VLAN and the port operates in manual VLAN assignment mode, the port forwards all received untagged packets in the voice VLAN. In normal mode, voice VLANs are vulnerable to traffic attacks. Malicious users might send 133