Intel S2600CP Technical Product Specification - Page 161
single line fuse
 |
View all Intel S2600CP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 161 highlights
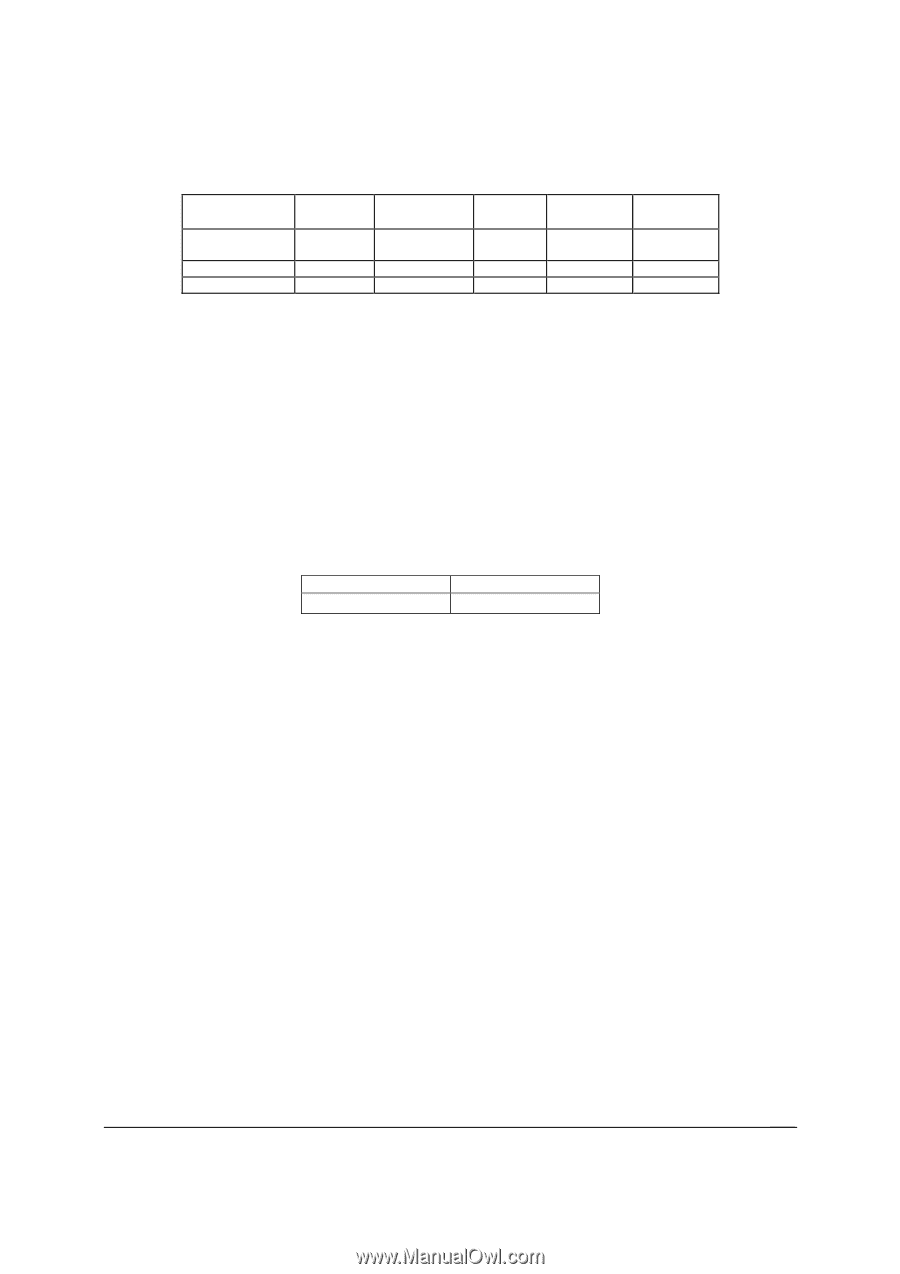
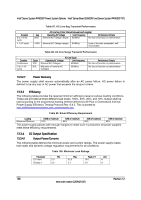
Intel® Server Board S2600CP and Server System P4000CP TPS Intel® Server System P4000CP Power System Options Table 95. AC Input Voltage Range Parameter MIN Rated VMAX Start up VAC Power Off VAC Voltage (110) 90 Vrms 100-127 Vrms 140 Vrms 85VAC +/4VAC 70VAC +/5VAC Voltage (220) Frequency 180 Vrms 47 Hz 200-240 Vrms 50/60 264 Vrms 63 Hz Notes: 1. Maximum input current at low input voltage range shall be measured at 90VAC, at max load. 2. Maximum input current at high input voltage range shall be measured at 180VAC, at max load. 3. This requirement is not to be used for determining agency input current markings. 13.3.2.4 AC Line Dropout/Holdup An AC line dropout is defined to be when the AC input drops to 0VAC at any phase of the AC line for any length of time. During an AC dropout the power supply meets dynamic voltage regulation requirements. An AC line dropout of any duration does not cause tripping of control signals or protection circuits. If the AC dropout lasts longer than the holdup time the power supply recovers and meets all turn on requirements. The power supply meets the AC dropout requirement over rated AC voltages and frequencies. A dropout of the AC line for any duration does not cause damage to the power supply. Table 96. AC Line Holdup Time Loading 70% Holdup time 12msec 13.3.2.4.1 AC Line 12VSBHoldup The 12VSB output voltage stays in regulation under its full load (static or dynamic) during an AC dropout of 70ms min (=12VSB holdup time) whether the power supply is in ON or OFF state (PSON asserted or de-asserted). 13.3.2.5 AC Line Fuse The power supply has one line fused in the single line fuse on the line (Hot) wire of the AC input. The line fusing is acceptable for all safety agency requirements. The input is a slow blow type. AC inrush current does not cause the AC line fuse to blow under any conditions. All protection circuits in the power supply does not cause the AC fuse to blow unless a component in the power supply has failed. This includes DC output load short conditions. 13.3.2.6 AC Line Transient Specification AC line transient conditions are defined as "sag" and "surge" conditions. "Sag" conditions are also commonly referred to as "brownout", these conditions is defined as the AC line voltage dropping below nominal voltage conditions. "Surge" is defined to refer to conditions when the AC line voltage rises above nominal voltage. The power supply meets the requirements under the following AC line sag and surge conditions. Revision 1.2 145 Intel order number G26942-003