Intel S2600CP Technical Product Specification - Page 45
Intel, Server Board S2600CP and Server System P4000CP TPS, Intel® Server Board S2600CP Functional
 |
View all Intel S2600CP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 45 highlights
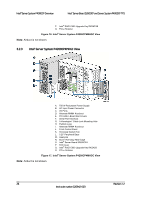
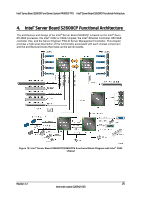
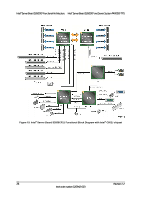
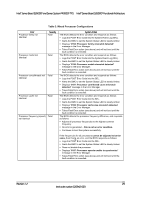
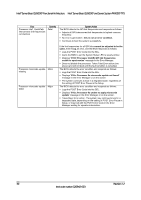
Intel® Server Board S2600CP and Server System P4000CP TPS Intel® Server Board S2600CP Functional Architecture Table 3. Mixed Processor Configurations Error Processor family not Identical Severity Fatal Processor model not Identical Fatal Processor cores/threads not Fatal identical Processor cache not identical Fatal Processor frequency (speed) Fatal not identical System Action The BIOS detects the error condition and responds as follows: Logs the POST Error Code into the System Event Log (SEL). Alerts the BMC to set the System Status LED to steady Amber. Displays "0194: Processor family mismatch detected" message in the Error Manager. Takes Fatal Error action (see above) and will not boot until the fault condition is remedied. The BIOS detects the error condition and responds as follows: Logs the POST Error Code into the System Event Log (SEL). Alerts the BMC to set the System Status LED to steady Amber. Displays "0196: Processor model mismatch detected" message in the Error Manager. Takes Fatal Error action (see above) and will not boot until the fault condition is remedied. The BIOS detects the error condition and responds as follows: Logs the POST Error Code into the SEL. Alerts the BMC to set the System Status LED to steady Amber. Displays "0191: Processor core/thread count mismatch detected" message in the Error Manager. Takes Fatal Error action (see above) and will not boot until the fault condition is remedied. The BIOS detects the error condition and responds as follows: Logs the POST Error Code into the SEL. Alerts the BMC to set the System Status LED to steady Amber. Displays "0192: Processor cache size mismatch detected message in the Error Manager. Takes Fatal Error action (see above) and will not boot until the fault condition is remedied. The BIOS detects the processor frequency difference, and responds as follows: Adjusts all processor frequencies to the highest common frequency. No error is generated - this is not an error condition. Continues to boot the system successfully. If the frequencies for all processors cannot be adjusted to be the same, then this is an error, and the BIOS responds as follows: Logs the POST Error Code into the SEL. Alerts the BMC to set the System Status LED to steady Amber. Does not disable the processor. Displays "0197: Processor speeds unable to synchronize" message in the Error Manager. Takes Fatal Error action (see above) and will not boot until the fault condition is remedied. Revision 1.2 29 Intel order number G26942-003