Dell PowerEdge 2970 Hardware Owner's Manual - Page 91
System Memory, General Memory Module Installation Guidelines - processor upgrade
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge 2970 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 91 highlights
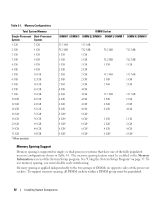
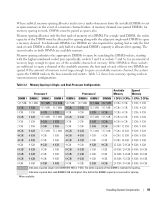
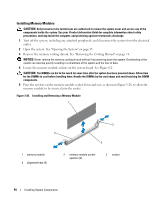
System Memory You can upgrade your system memory to a maximum of 32 GB (for a one-processor configuration) or 64 GB (for a two-processor configuration) by installing 667-MHz registered parity DDR-II memory modules (DIMMs) in sets of 512-MB, 1-GB, 2-GB, 4-GB, or 8-GB (when available) modules. The memory sockets are located on the system board under the cooling shroud and are split into two separate groups of four sockets each. Each four-socket group is adjacent to its respective processor. Your system hardware supports Non-Uniform Memory Architecture (NUMA). Each processor has its own memory controller and local memory for reduced access times, but it can also access memory from another processor. This architecture improves system performance if an operating system is installed that supports this feature. NOTICE: To enable NUMA, run the System Setup program and disable the Node Interleaving option. See "Using the System Setup Program" on page 37. General Memory Module Installation Guidelines To ensure optimal performance of your system, observe the following guidelines when configuring your system memory. • Memory must be installed in configurations of two, four, or eight DIMMs. The minimum configuration for a two-processor system is four DIMMs. • DIMMs must be installed in matched pairs of identical speed, technology, and size in the following pairs of sockets: - DIMM 1 and DIMM 2 - DIMM 3 and DIMM 4 - DIMM 5 and DIMM 6 - DIMM 7 and DIMM 8 • Minimum configurations must occupy the lower-numbered sockets (DIMM 1 and DIMM 2 for a oneprocessor configuration and also DIMM5 and DIMM6 for a two-processor configuration). • Within a DIMM group, a pair of DIMMs of one size can be mixed with a pair of DIMMs of a different size (N+3, or up to three DIMM sizes larger). Larger capacity DIMMs must occupy the lowernumbered sockets. Table 3-1 shows the available memory configurations following these guidelines. Installing System Components 91