HP 9000 rp4410-4 User Service Guide, Fifth Edition - HP 9000 rp4410/4440 - Page 108
Configuring the iLO MP LAN Using ARP Ping, iLO MP Log
 |
View all HP 9000 rp4410-4 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 108 highlights
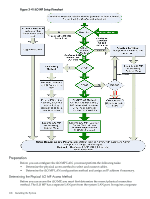
TIP: HP recommends using the DHCP and DNS method to simplify access to the iLO MP. When you use DHCP and DNS, connect to the iLO MP by entering the DNS name in the browser rather than an IP address only if the following conditions apply: • DHCP must be enabled (DHCP is enabled by default). • You are using a DHCP server that provides the domain name and the primary DNS server IP address. • The primary DNS server accepts dynamic DNS (DDNS) updates. • The primary DNS server IP address has been configured through the DHCP server. To configure the iLO MP using DHCP and DNS, follow these steps: 1. Obtain the factory-set DNS name from the toe-tag on the server. The DNS name is 14 characters long, consisting of the letters mp followed by the 12 characters of the MAC address, for example: mp0014c29c064f. This address is assigned to the iLO MP hardware. The iLO MP has a unique MAC address that identifies the hardware on the network. 2. Connect the LAN cable from the server to an active network port. 3. Apply ac power to the server (if not already done). 4. Open a browser, telnet, or SSH client and enter the DNS name. The iLO MP Log In window opens. 5. Log in to the iLO MP. See "Logging In to the iLO MP" (page 110). Configuring the iLO MP LAN Using ARP Ping The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) and Packet Internet Grouper (Ping) utility uses ARP packets to ping, or discover, a device on the local network segment. The IP address you assign to the server must use the same network segment, or subnet, as the computer assigning the address. ARP does not work across routed or switched networks. ARP Ping operational issues include the following: • You can use ARP Ping regardless of the status of DHCP, unless an IP address has ever been acquired using DHCP. • When ARP Ping is successful, DHCP status is disabled. • Some DHCP server options can cause the apparent issuance of ARP Ping to the iLO MP which will negate the DHCP/DDNS method. • The PC and the server must be on the same physical subnet. • When a new server is first booted, DHCP is automatically available (factory-set default); but ARP Ping does not start until three minutes after the iLO MP is booted. This applies to every subsequent boot of the iLO MP until an IP address is obtained by DHCP or has been assigned using the LC command, or ARP Ping succeeds. There are two ways to use the ARP Ping utility: • Connect a PC to the network that is on the same physical subnet as the server and run the ARP Ping commands from the PC. • Locate an existing server on the network, log into it, and run the ARP Ping commands from the server. Table 3-16 lists the ARP Ping commands. 108 Installing the System