Intel SE7525GP2 Product Specification - Page 117
Direct Platform Control IPMI over LAN
 |
View all Intel SE7525GP2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 117 highlights
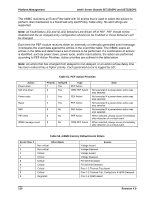
Intel® Server Boards SE7320SP2 and SE7525GP2 Platform Management In addition, the mBMC supports LAN alerting in the form of SNMP traps that conform to the IPMI Platform Event Trap (PET) format. Table 49. LAN Channel Capacity LAN CHANNEL Capability Number of Sessions Number of Users User User Password Privilege Levels Authentication Types Number of LAN Alert Destinations Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Options 1 1 Name NULL (anonymous) Configurable User, Operator, Administrator MD5 1 Gratuitous ARP 5.2.5 Direct Platform Control (IPMI over LAN) Direct Platform Control provides a mechanism for delivering IPMI Messages directly to the management controllers via a LAN connection. The NICs and the management controllers remain active on standby power, enabling the IPMI Messaging when the system is powered up, powered down, and in a system sleep state. This allows a remote console application to be able to access the management controller capabilities, including: ƒ Power on/off and reset control with the ability to set BIOS boot flags ƒ FRU, SDR, and SEL access ƒ BMC configuration access ƒ Remote NMI generation ƒ Ability to transfer IPMI messages between the LAN interface and other interfaces, such as the System Interface, IPMB, and PCI SMBus. This capability enables messages to be delivered to system management software, and provides the ability to access sensors and FRU information on other management controllers. IPMI Messages are encapsulated in a packet format called RMCP (Remote Management Control Protocol). The Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF) has defined RMCP for supporting pre-OS and OS-absent management. RMCP is a simple request-response protocol that can be delivered using UDP datagrams. IPMI-over-LAN uses version 1 of the RMCP protocol and packet format. UDP port 26Fh is a 'well known port' address that is specified to carry RMCP (Remote Management Control Protocol) formatted UDP datagrams. The onboard Intel network interface controllers contain circuitry that enables detecting and capturing RMCP packets that are received on Port 26Fh and making them available to the management controller via a 'sideband' interface that is separate from the PCI interface to the NIC. Similarly, the management controller can use the side-band interface to send packets from Port 26Fh, as shown in the following figure. Revision 4.0 105