Intel SE7525GP2 Product Specification - Page 45
Legacy Interrupt Sources, 6.3.4, Serialized IRQ Support, 6.3.5, IRQ Scan for PCI IRQ
 |
View all Intel SE7525GP2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 45 highlights
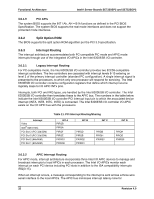
Intel® Server Boards SE7320SP2 and SE7525GP2 Functional Architecture compatibility interrupt sources. The I/O APICs can also supply greater than 16 interrupt levels to the processor(s). This APIC bus consists of an APIC clock and two bidirectional data lines. 3.6.3.3 Legacy Interrupt Sources The table below recommends the logical interrupt mapping of interrupt sources. The actual interrupt map is defined using configuration registers in the Intel® 6300ESB I/O controller. Table 12. Interrupt Definitions ISA Interrupt INTR NMI IRQ0 IRQ1 IRQ2 IRQ3 IRQ4 IRQ5 IRQ6 IRQ7 IRQ8_L IRQ9 IRQ10 IRQ11 IRQ12 IRQ13 IRQ14 IRQ15 SMI* Processor interrupt Description NMI to processor System timer Keyboard interrupt Slave PIC Serial port 1 or 2 interrupt from SUPER I/O device, user-configurable Serial port 1 or 2 interrupt from SUPER I/O device, user-configurable Parallel Port / Generic Floppy disk Generic Active low RTC interrupt SCI* Generic Generic Mouse interrupt Floating point processor Compatibility IDE interrupt from primary channel IDE devices 0 and 1 Secondary IDE cable System management interrupt. General purpose indicator sourced by the 6300ESB to the processors. 3.6.3.4 Serialized IRQ Support The server boards support a serialized interrupt delivery mechanism. Serialized Interrupt Requests (SERIRQ) consists of a start frame, a minimum of 17 IRQ / data channels, and a stop frame. Any slave device in the quiet mode may initiate the start frame. While in the continuous mode, the start frame is initiated by the host controller. 3.6.3.5 IRQ Scan for PCI IRQ The IRQ / data frame structure includes the ability to handle up to 32 sampling channels with the standard implementation using the minimum 17 sampling channels. The server boards have an external PCI interrupt serializer for PCI IRQ scan mechanism of Intel 6300ESB I/O controller to support 16 PCI IRQs. Revision 4.0 33