Intel SE7525GP2 Product Specification - Page 94
Flash Update Utility
 |
View all Intel SE7525GP2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 94 highlights
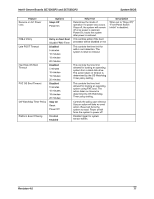
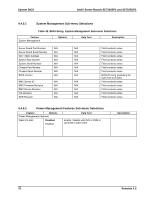
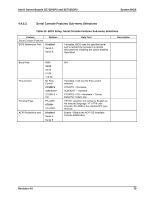
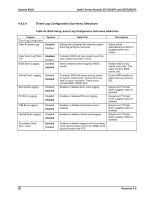
System BIOS Intel® Server Boards SE7320SP2 and SE7525GP2 The BIOS relies on specialized hardware and additional flash space to accomplish online update/rolling of the BIOS. To this end, the flash is divided into two partitions, primary and secondary. The active partition from which the system boots is referred to as the primary partition. The AMI FLASH update suite and Intel online updates preserve the existing BIOS image on the primary partition. BIOS updates are diverted to the secondary partition. After the update is complete, a notification flag is set. During the subsequent boot following the BIOS update, the system first continues to attempt to boot from the primary BIOS partition. On determining that a BIOS update occurred in the previous boot, the system then attempts to boot from the new BIOS. If a failure happens while booting to the new BIOS, the specialized hardware on the system switches back to the primary BIOS partition, thus affecting a "rollback". If a user wishes to force the system to boot to the primary bank, the jumper at J29 can be used. In the default jumper position with pins 1-2 covered, the rolling BIOS configuration is automatic. If the jumper is moved to cover pins 2-3, then the system will boot to the primary bank every time. The rolling one-boot update feature applies to all the update mechanisms discussed in the following sections. 4.7 Flash Update Utility Server platforms support a DOS-based firmware update utility. This utility loads a fresh copy of the BIOS into the flash ROM. The BIOS update may affect the following items: ƒ The system BIOS, including the recovery code, setup utility and strings. ƒ Onboard video BIOS, SCSI BIOS, and other option ROMS for the devices embedded on the server board. ƒ OEM binary area. ƒ Microcode updates. 4.7.1 Flash BIOS The BIOS flash utility is compatible with DOS, Microsoft* Windows* 2000/2003/XP, Linux and EFI operating environments. An afuXXX AMI Firmware Update utility (such as AFUDOS, AFUWIN, AFULNX, or AFUEFI) is required for a BIOS update. The format and usage of the afuXXX utility is as follows: afuXXX /i [/n] [/p[b][n][c]] [/r] [/s] [/k] [/q] [/h] 82 Revision 4.0