Intel SE7525GP2 Product Specification - Page 97
BIOS Recovery
 |
View all Intel SE7525GP2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 97 highlights
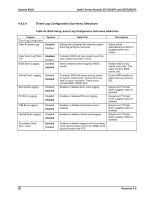
Intel® Server Boards SE7320SP2 and SE7525GP2 System BIOS 4.7.3.1 BIOS Recovery The BIOS has a ROM image size of 2 MB. A standard 1.44 MB floppy diskette cannot hold the entire ROM file due to the large file size. To compensate for this, a Multi-disk recovery method is available for BIOS recover (see Section 4.7.3.2 for further details). The BIOS contains a primary and secondary partition, and can support rolling BIOS updates (see Section 4.6 for details). The recovery process performs an update on the secondary partition in the same fashion that the normal flash update process updates the secondary partition. After recovery is complete and the power is cycled to the system, the BIOS partitions switch and the code executing POST will be the code that was just flashed from the recovery media. The BIOS is made up of a boot block recovery section, a main BIOS section, an OEM logo/user binary section, and an NVRAM section. The NVRAM section will either be preserved or destroyed based on a hot key press during invocation of the recovery. All the other sections of the secondary BIOS will be updated during the recovery process. If an OEM wishes to preserve the OEM section across an update, it is recommended that the OEM modify the provided AMIBOOT.ROM file with the user binary or OEM logo tools before performing the recovery. A BIOS recovery can be accomplished from one of the following devices: a standard 1.44 or 2.88 MB floppy drive, an USB Disk-On-Key, or an ATAPI CD-ROM/DVD. The recovery media must include the BIOS image file, AMIBOOT.ROM. The recovery mode procedure is as follows: ƒ Insert or plug-in the recovery media with the AMIBOOT.ROM file. ƒ Power on the system. When progress code E9 is displayed on port 80h, the system will detect the recovery media (if there is no image file present, the system will cycle through progress code F1 to EF). ƒ When F3 is displayed on port 80h, the system will read the BIOS image file. ƒ The screen will display flash progress and indicate whether the NVRAM and CMOS have been destroyed. ƒ When recovery mode is complete, the system will halt and the system can be powered off. Note: Three different hot-keys can be invoked: ƒ - Recovery with CMOS destroyed and NVRAM preserved. ƒ - Recovery with both CMOS and NVRAM preserved. ƒ - Recovery with both CMOS and NVRAM destroyed. Revision 4.0 85