Garmin GPSMAP 296 Pilot's Guide - Page 146
Learning About GPS, Common GPS Terms, What is Differential GPS DGPS?, Differential Field
 |
View all Garmin GPSMAP 296 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 146 highlights
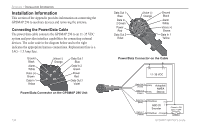
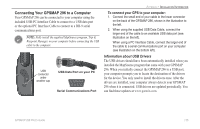
APPENDIX > LEARNING ABOUT GPS Learning About GPS The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system made up of a network of 24 satellites placed into orbit by the United States Department of Defense. GPS was originally intended for military applications, but in the 1980s, the government made the system available for civilian use. GPS works in any weather conditions, anywhere in the world, 24 hours a day. There are no subscription fees or setup charges to use GPS. For more information refer to the Garmin Web site at www. garmin.com and also read the GPS Guide for Beginners, which can be found on the Web site at http://www.garmin.com/aboutGPS/manual.html. Common GPS Terms Initialize-the first time a GPS receiver orients itself to its current location and collects data. After the receiver is initialized, it remembers its location and acquires a location more quickly. Location-an exact, unique location based on geographic coordinates (Latitude and Longitude). Route-A group of waypoints entered into the GPS receiver in the sequence you want to navigate them. Waypoint-a location you store in your GPS. What is Differential GPS (DGPS)? The United States and Canadian governments (among others) have set up Differential GPS (DGPS) stations to transmit correction signals. They are operational in coastal areas and on many navigable river systems. The DGPS system is available for use without a fee, but you do need additional equipment to receive DGPS signals: A beacon receiver compatible with the RTCM format sentences supported by your Garmin GPS is needed to use DGPS. Refer to the United States Coast Guard's Web site (http://www. navcen.uscg.gov/) for locations and status of the differential stations. Differential Field Differential receiver status is indicated in the bottom left field of the GPS Page and shows one of the following conditions: • None-no optional beacon receiver is attached or enabled on the Interface sub tab on the Main Menu or WAAS is turned off. • Searching for WAAS-WAAS is enabled and the receiver is searching for WAAS signal. • Using WAAS-WAAS capability is enabled and the unit is receiving WAAS corrections. 138 GPSMAP 296 Pilot's Guide