Lenovo ThinkServer RD330 MegaRAID SAS Software User Guide - Page 262
Stripe size, Read policy, Write policy, I/O policy, Access policy
 |
View all Lenovo ThinkServer RD330 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 262 highlights
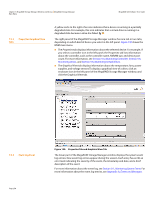
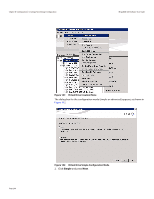
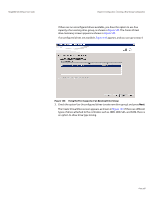
Chapter 8: Configuration | Creating a New Storage Configuration MegaRAID SAS Software User Guide NOTE: BGI is supported only for RAID 5 and RAID 6 and not for any other RAID levels. New RAID 5 virtual drives require at least five drives for a background initialization to start. New RAID 6 virtual drives require at least seven drives for a background initialization to start. If there are fewer drives, the background initialization does not start. Stripe size: Stripe sizes of 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, and 1024 KB are supported. The default is 64 KB. For more information, see the striping entry in the Glossary. Read policy: Specify the read policy for this virtual drive: - Always read ahead: Read ahead capability allows the controller to read sequentially ahead of requested data and to store the additional data in cache memory, anticipating that the data will be needed soon. This speeds up reads for sequential data, but there is little improvement when accessing random data. - No read ahead: (the default) Disables the read ahead capability. Write policy: Specify the write policy for this virtual drive: - Write Through: In this mode, the controller sends a data transfer completion signal to the host when the drive subsystem has received all of the data in a transaction. This option eliminates the risk of losing cached data in case of power failure. - Always Write Back: In this mode, the controller sends a data transfer completion signal to the host when the controller cache has received all of the data in a transaction. - Write Back with BBU: (the default) In this mode, the controller enables Write Back caching when the battery backup unit (BBU) is installed and charged. It provides a good balance between data protection and performance. NOTE: The Write Policy depends on the status of the battery backup unit (BBU). If the BBU is not present, is low, is failed, or is being charged, the default Write Policy will switch to Write Through, which provides better data protection. I/O policy: The I/O policy applies to reads on a specific virtual drive. It does not affect the read ahead cache. - Cached IO: In this mode, all reads are buffered in cache memory. - Direct IO: (the default) In this mode, reads are not buffered in cache memory. Data is transferred to the cache and the host concurrently. If the same data block is read again, it comes from cache memory. Cached IO provides faster processing, and Direct IO ensures that the cache and the host contain the same data. Access policy: Select the type of data access that is allowed for this virtual drive. - Read/Write: (the default) Allow read/write access. This is the default. - Read Only: Allow read-only access. - Blocked: Do not allow access. Page 262