Lenovo ThinkServer RD330 MegaRAID SAS Software User Guide - Page 27
Disk Spanning, 4.11.1, Spanning for RAID 00, RAID 10, RAID 50, and RAID 60
 |
View all Lenovo ThinkServer RD330 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 27 highlights
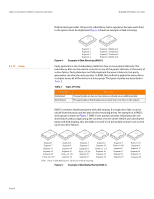
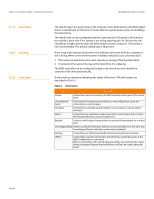
MegaRAID SAS Software User Guide 2.4.11 Disk Spanning Chapter 2: Introduction to RAID | Components and Features Disk spanning allows multiple drives to function like one big drive. Spanning overcomes lack of disk space and simplifies storage management by combining existing resources or adding relatively inexpensive resources. For example, four 20 GB drives can be combined to appear to the operating system as a single 80 GB drive. Spanning alone does not provide reliability or performance enhancements. Spanned virtual drives must have the same stripe size and must be contiguous. In Figure 6, RAID 1 drive groups are turned into a RAID 10 drive group. NOTE: Make sure that the spans are in different backplanes, so that if one span fails, you do not lose the whole drive group. 2.4.11.1 Spanning for RAID 00, RAID 10, RAID 50, and RAID 60 60 GB 60 GB Can Be Accessed as One 120-GB Drive 60 GB 60 GB Can Be Accessed as One 120-GB Drive Figure 6: Example of Disk Spanning Spanning two contiguous RAID 0 virtual drives does not produce a new RAID level or add fault tolerance. It does increase the capacity of the virtual drive and improves performance by doubling the number of spindles. Table 3 describes how to configure RAID 00, RAID 10, RAID 50, and RAID 60 by spanning. The virtual drives must have the same stripe size and the maximum number of spans is eight. The full drive capacity is used when you span virtual drives; you cannot specify a smaller drive capacity. See Chapter 8, Configuration for detailed procedures for configuring drive groups and virtual drives, and spanning the drives. Table 3: Spanning for RAID 10, RAID 50, and RAID 60 Level 00 10 50 60 Description Configure RAID 00 by spanning two contiguous RAID 0 virtual drives, up to the maximum number of supported devices for the controller. Configure RAID 10 by spanning two contiguous RAID 1 virtual drives, up to the maximum number of supported devices for the controller. RAID 10 supports a maximum of eight spans. You must use an even number of drives in each RAID virtual drive in the span. The RAID 1 virtual drives must have the same stripe size. Configure RAID 50 by spanning two contiguous RAID 5 virtual drives. The RAID 5 virtual drives must have the same stripe size. Configure RAID 60 by spanning two contiguous RAID 6 virtual drives. The RAID 6 virtual drives must have the same stripe size. Page 27