Lenovo ThinkServer RD330 MegaRAID SAS Software User Guide - Page 37
RAID 00 Drive Group Example with Two Drives, Table 12, RAID 10 Overview
 |
View all Lenovo ThinkServer RD330 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
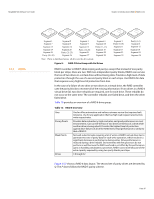
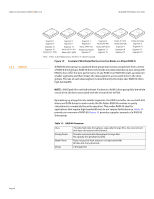
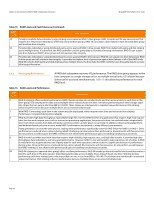
MegaRAID SAS Software User Guide Chapter 2: Introduction to RAID | RAID Levels 2.5.8 RAID 10 RAID 00 Segment 1 Segment 2 Segment 9 Segment 10 Segment 17 Segment 18 ... Segment 3 Segment 4 Segment 11 Segment 12 Segment 19 Segment 20 ... Segment 5 Segment 13 Segment 21 ... Segment 6 Segment 14 Segment 22 Segment 7 Segment 15 Segment 23 ... Segment 8 Segment 16 Segment 24 RAID 0 RAID 0 RAID 0 RAID 0 Figure 11: RAID 00 Drive Group Example with Two Drives RAID 0 RAID 10 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1, and consists of stripes across mirrored drives. RAID 10 breaks up data into smaller blocks and then mirrors the blocks of data to each RAID 1 drive group. The first RAID 1 drive in each drive group then duplicates its data to the second drive. The size of each block is determined by the stripe size parameter, which is set during the creation of the RAID set. The RAID 1 virtual drives must have the same stripe size. Spanning is used because one virtual drive is defined across more than one drive group. Virtual drives defined across multiple RAID 1 level drive groups are referred to as RAID level 10, (1+0). Data is striped across drive groups to increase performance by enabling access to multiple drive groups simultaneously. Each spanned RAID 10 virtual drive can tolerate multiple drive failures, as long as each failure is in a separate drive group. If there are drive failures, less than total drive capacity is available. Configure RAID 10 by spanning two contiguous RAID 1 virtual drives, up to the maximum number of supported devices for the controller. RAID 10 supports a maximum of eight spans, with a maximum of 32 drives per span. You must use an even number of drives in each RAID 10 virtual drive in the span. NOTE: Other factors, such as the type of controller, can restrict the number of drives supported by RAID 10 virtual drives. Table 12 provides an overview of RAID 10. Table 12: RAID 10 Overview Uses Strong Points Weak Points Drives Appropriate when used with data storage that needs 100 percent redundancy of mirrored drive groups and that also needs the enhanced I/O performance of RAID 0 (striped drive groups.) RAID 10 works well for medium-sized databases or any environment that requires a higher degree of fault tolerance and moderate to medium capacity. Provides both high data transfer rates and complete data redundancy. Requires twice as many drives as all other RAID levels except RAID 1. 4 - The maximum number of drives supported by the controller (using an even number of drives in each RAID 10 virtual drive in the span) Page 37