HP NetServer AA 4000 HP AA HP Netserver 4000 Reference Guide - Page 119
Other MTC Tools
 |
View all HP NetServer AA 4000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 119 highlights
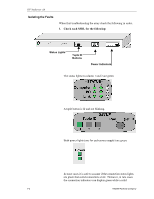
Other MTC Tools Ch 7: Bsic Troubleshooting NOTE If you are monitoring the HP AA array using the Remote Marathon Manager, you only have access to the Marathon Manager and the Windows NT Event Viewer information. Marathon provides other tools with the system which are not necessarily troubleshooting tools, but they can be great for information gathering. MTCEINFO can provide the details of the Ethernet cards and MTCCPYNT can be used to bring back an OS directory, in effect, restore, one that was "saved" by the same utility. • Boot Process - IOP When in doubt about what component is failing, watch the Marathon boot process from POST of the server to the POST of the system, and at the same time, look at what the error logs are recording, and watch the Marathon Manager console. The above slide shows the boot process for the IOPs. Follow it along to make sure each step is getting completed, and if not find the component preventing any of the steps. • MTCTEST If the Marathon Manager were showing a failed Marathon Interface card than it would be the normal reaction to replace the MIC. There could be a problem with the Marathon configuration and the MIC should be further tested. MTCTEST has the ability to test the MIC locally and in tandem with another MIC. This test should be attempted outside of the Marathon array before replacing the card. The test is run from a DOS floppy disk and a second disk would be needed to test against another MIC for communication. Network Server Division 7-3