HP NetServer AA 4000 HP AA HP Netserver 4000 Reference Guide - Page 15
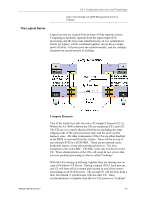
The Compute Elements, The SSDLs, The I/O Processors
 |
View all HP NetServer AA 4000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
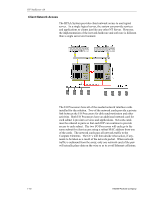
Ch 1: Architecture Overview and Terminology Division of Labor The compute elements and the I/O processors have very distinct roles and therefore have different performance characteristics. If the array was going to do nothing more than run Windows NT without any applications, then the memory requirements are minimal. The array can be functional with 64 MB of memory for each node. This serves to prove that the AA 4000 software itself is not memory intensive and does require a significant amount of server resources. The Compute Elements The compute element functions with just the CPU and the memory. The server is sized for the maximum amounts of CPU and memory required for the application that stays within the limits of the memory support of the physical server and the fact that the HP AA 4000 software currently supports one CPU and a maximum of 2 GB of system memory. The system will generate I/O requests, but they are immediately intercepted by the HP AA 4000 software and transferred to the IOP via the MICs, cables, and SSDLs. This creates a very low overhead for I/O operations on the CE. The SSDLs These two components are nothing more than I/O routers. By requiring that the nodes be attached to specific ports, what little software function there is in the SSDLs is easily maintained and does not have to be concerned with any kind of routing scheme or mesh. The SSDLs are for making sure the data is transferred from each CE to both IOPs by simply providing a path. The HP AA 4000 software is responsible for the integrity of the data between the nodes and largely does this through checksums (EDCs) at the end of each packet transfer. The I/O Processors Here a different kind of server activity takes place. The I/O Processors do not run any applications other than simple management software added by the customer. They are complex I/O controllers that for lack of an easier solution happen to be running Windows NT. They are not in lock-step with each other, but instead, maintain disk synchronization through a HP AA 4000 software disk partition on each logical disk the CE uses. These are not CPU or memory intensive operations. As it turns out, the disk activity itself, as in most optimized server environments, can be the bottleneck if there is one. CAUTION It is possible to run applications on the IOPs. However, this impacts the reliability of the overall system. HP strongly recommends that other applications not be run on the IOPs but will continue to support the array. Network Server Division 1-9