Symantec 10521148 Implementation Guide - Page 41
Deployment using in-line mode, Comparing in-line mode to passive mode, Interface grouping
 |
View all Symantec 10521148 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 41 highlights
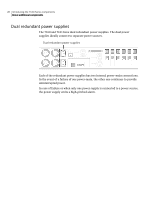
Deploying the 7100 Series 33 Deployment options The 7100 Series node receives incoming network traffic on one interface of the in-line pair, then the Network Security detection software analyzes the traffic for malicious content. Once the analysis is complete, Network Security sends the traffic out on the other interface. You can select alerting or blocking mode for each in-line pair by customizing and applying a protection policy to the in-line pair. A protection policy is a collection of attack types combined with configurable responses. Some protection policies support blocking, and others do not. You can only enable blocking for in-line pairs. For more information about protection policies, see "About protection policies" on page 116, and the Symantec Network Security Administration Guide. Deployment using in-line mode The initial setup for in-line mode requires an interruption to network traffic while you make the necessary cabling changes. The appliance must be physically connected as part of the network path to block malicious traffic from reaching its target inside your network. See "Cabling" on page 49. Comparing in-line mode to passive mode Table 3-1 illustrates the differences and similarities between in-line mode and passive mode on the Symantec Network Security 7100 Series. Table 3-1 In-line mode compared to passive mode Feature or characteristic Alerting Blocking Interrupts traffic during setup Number of interfaces used In-line mode Yes Yes Yes 2 Passive mode Yes No No 1 Interface grouping You can use interface grouping when asymmetric traffic patterns appear in your network. Asymmetric routing occurs when network traffic to and from a given IP address does not follow the same path. Interface grouping is the solution to this problem.