D-Link DWS-3160-24TC DWS-3160 Series Web UI Reference Guide - Page 504
Certificate Generation on the Access Point
 |
View all D-Link DWS-3160-24TC manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 504 highlights
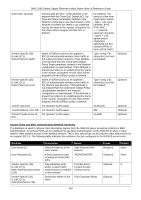
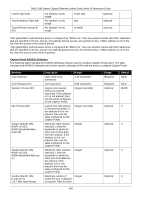
DWS-3160 Series Gigabit Ethernet Unified Switch Web UI Reference Guide Each wireless device has a copy of a certificate of the device with which it needs to communicate. During TLS connection establishment the Wireless devices compare the certificate received on the connection setup with all available loaded certificates for other wireless devices. If a matching certificate is found then the certificate verification succeeds. The verification function does not attempt to correlate the IP address of the device with the certificate and it does not check the certificate expiration date. The TLS connections are configured to validate the certificates only on the initial connection setup. The connection reauthentications don't trigger new certificate validation attempts. Certificate Generation on the Access Point: The AP auto-generates an X.509 certificate when it boots. At boot time the AP checks whether the key file and the certificate file already exists. If the files exist then the AP uses them, otherwise the AP generates the files. The /etc/uwskey.pem file contains the 1024 bit private key. The /etc/uwscert.pem file contains the X.509 certificate. In order to regenerate the AP certificates the administrator may issue a "factory-reset" command on the AP or delete the two files from the file system and reboot the AP. Certificate Generation on the Switch: The Switch auto-generates an X.509 certificate and other key files when it boots. At boot time the Switch checks whether the certificate and key files exist, and if they don't then the Switch generates the files. The administrator can re-generate the X.509 certificates used by the Wireless component. Note that Diffie-Hellman keys are not regenerated. The wireless feature should be disabled while the keys are being regenerated. If mutual authentication is enabled then the Switch must be re-provisioned before it can join the cluster. IP Address Assignment The Wireless Switches are assigned IP addresses by the administrator. The routing package is included into the product and the routing is enabled by default. Besides the existing System interface, the administrator may create a routing interface optionally. The wireless software automatically selects the IP Address of the lowest interface index. The System interface is always the interface with the lowest index "1". If the System interface is deleted then the software automatically selects the IP address of a lowest index routing interface. If no interfaces are defined then the wireless function is disabled. Disabling the interface or changing the IP address of the interface disables the wireless function. If another interface exists then the wireless function starts using it automatically. Once an interface is selected the wireless function continues to use that interface until the interface goes down. Changing the IP address of the network interface automatically disables and re-enables the wireless function. The administrator has the option to disable automatic IP address assignment for the Wireless function and enter a static IPv4 address. The IP address must be the same as an address of an active routing interface in order for the Wireless function to work. If the interface with the specified address doesn't exist or is not active then the Wireless function is disabled and the WLAN Switch Disable Reason is set to "No Active Interface for Statically Configured IP Address". If the static IP address is configured when the Wireless feature is already enabled then if the configured static IP address is different from the current IP address used by the Wireless feature then the Wireless feature is automatically disabled and re-enabled with the new IP address. If the configured static IP address is already being used by the Wireless feature then the Wireless feature is not disabled and service to the wireless clients is not interrupted. IP Tunnel versus MBA and IMPB When Wireless Switches enables IP tunneling for wireless clients, the MAC of the wireless tunnel client has the highest priority. MBA and IMPB will not work to limit the wireless tunnel client MAC. In addition, when a wireless tunnel client is added by Wireless Switch, the Wireless Switch will notify the MBA module to remove the client MAC if it added the MAC. 499