Sony XDSPD2000 User Manual (XDS-PD1000 and XDS-PD2000 Operation Manual for Fir - Page 94
Standard commands, <type-code> can be any of the following. However,
 |
View all Sony XDSPD2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 94 highlights
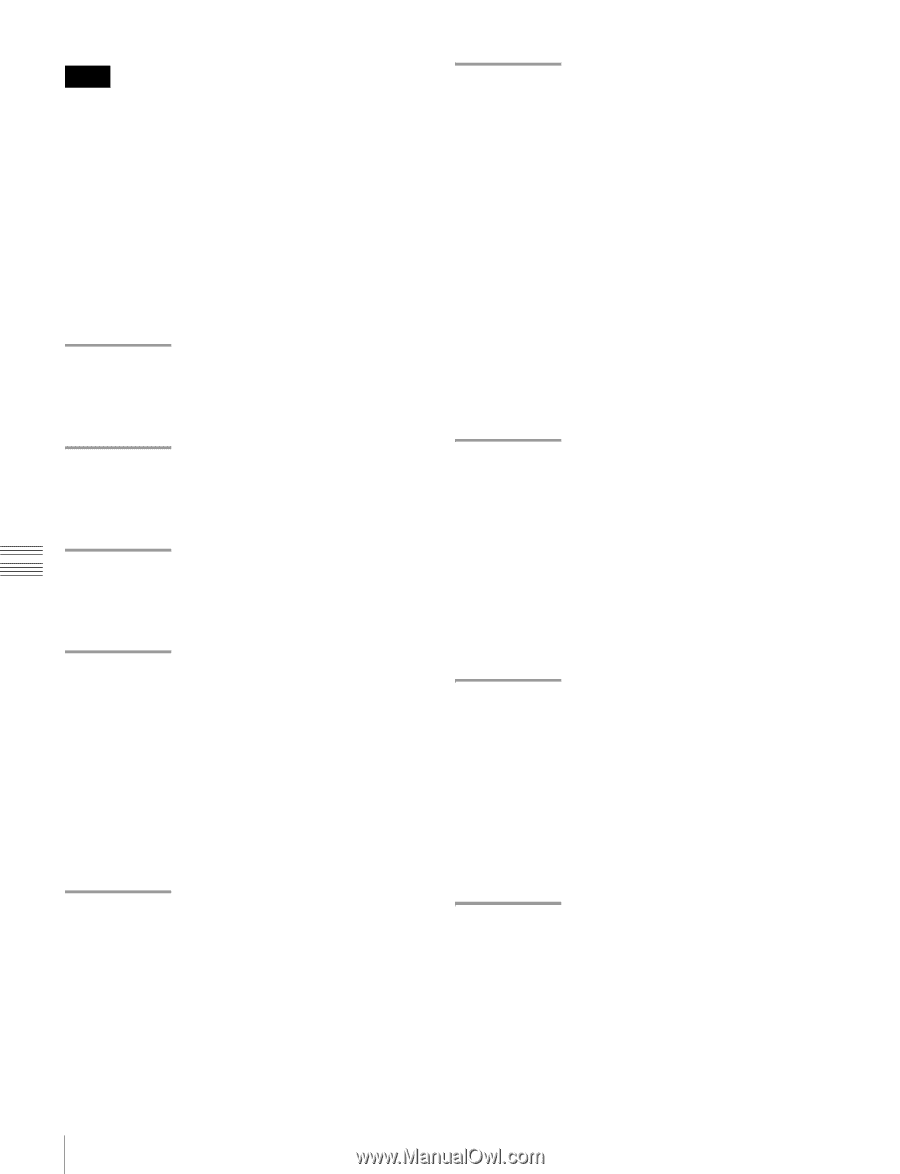
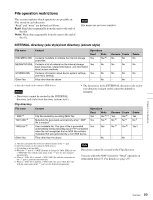
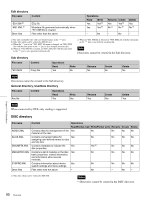
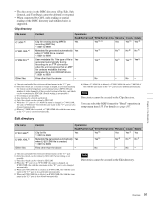
Notes • To execute FTP commands, you must install application software such as Content Browser on your computer. • The commands supported by application software vary. • An FTP client software that supports UTF-8 is required to use Unicode characters other than ASCII characters. Command prompt FTP commands do not support UTF-8. Standard commands In the command syntax, means a space, entered by pressing the space bar, and means a new line, entered by pressing the Enter key. USER Send this command to begin the login process. Command syntax: USER Input example: USER admin PASS Send this command to complete the login process. Command syntax: PASS Input example: PASS xds-1000 QUIT Terminates the FTP connection. If a file is being transferred, terminates after completion of the transfer. Command syntax: QUIT PORT Specifies the IP address and port to which this unit should connect for the next file transfer (for data transfer from this unit). Command syntax: PORT • h1 (most significant byte) to h4 (least significant byte): IP address • p1 (most significant byte), p2 (least significant byte): Port number Input example: PORT 10,0,0,1,242,48 (IP address: 10.0.0.1, Port number: 62000) PASV This command requests this unit to "listen" on a data port (which is not its default data port). (It puts this unit into passive mode, waiting for the remote computer to make a data connection.) Command syntax: PASV TYPE Specifies the type of data to be transferred. Command syntax: TYPE can be any of the following. However, for XDS devices, data is always transferred as "I", regardless of the type-code specification. • A: ASCII - N: Non-print - T: Telnet format - C: ASA Carriage Control • E: EBCDIC - N: Non-print - T: Telnet format - C: ASA Carriage Control • I: IMAGE (Binary) (default) • L: LOCAL BYTE - SIZE: byte size Input example: TYPE I STRU Specifies the data structure. Command syntax: STRU can be any of the following. However, for XDS devices, the structure is always "F", regardless of the structure-code specification. • F: File structure (default) • R: Record structure • P: Page structure Input example: STRU F MODE Specifies the transfer mode. Command syntax: MODE can be any of the following. However, for XDS devices, the mode is always "S", regardless of the mode-code specification. • S: Stream mode (default) • B: Block mode • C: Compressed mode Input example: MODE S LIST Sends a list of files from this unit to the remote computer. Command syntax: LIST can be any of the following. • -a: Also display file names that begin with "." • -F: Append "/" to directory names. Chapter 6 File Operations 94 FTP File Operations