ZyXEL V630 User Guide - Page 118
Wireless Security Overview, 11.2.1 SSID, WPA2-PSK, Compatible
 |
View all ZyXEL V630 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 118 highlights
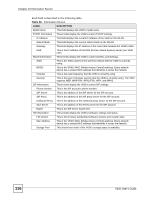
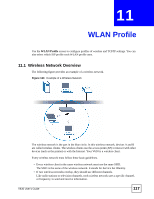
Chapter 11 WLAN Profile • Every wireless client in the same wireless network must use security compatible with the AP. Security stops unauthorized devices from using the wireless network. It can also protect the information that is sent in the wireless network. 11.2 Wireless Security Overview The following table shows the relative strengths of common types of wireless security. Use the strongest security that every wireless client in the wireless network supports. Table 97 Wireless Security Types NO RADIUS SERVER RADIUS SERVER Weakest No Security Static WEP WPA-PSK WPA Strongest WPA2-PSK WPA2 If you have a RADIUS server, you can use WPA or WPA2 so users have to log into the wireless network before using it. This is called user authentication. RADIUS servers are more common in businesses (WPA and WPA2 are also called the enterprise version of WPA). If you do not have a RADIUS server, the strongest wireless security you can use is WPA2PSK (WPA2-PSK and WPA-PSK are also known as the personal version of WPA). It is recommended that wireless networks use WPA-PSK, WPA, or stronger security. WEP is better than no security, but it is still possible for unauthorized devices to figure out the original information pretty quickly. When you select WPA2 or WPA2-PSK in your V630, you can also select an option (WPA Compatible) to support WPA as well. In this case, if some wireless clients support WPA and some support WPA2, you should set up WPA2-PSK or WPA2 (depending on the type of wireless network login) and select the WPA Compatible option in the V630. 11.2.1 SSID Normally, the AP acts like a beacon and regularly broadcasts the SSID in the area. You can hide the SSID instead, in which case the AP does not broadcast the SSID. In addition, you should change the default SSID to something that is difficult to guess. This type of security is fairly weak, however, because there are ways for unauthorized devices to get the SSID. In addition, unauthorized devices can still see the information that is sent in the wireless network. 118 V630 User's Guide