Casio CFX-9800G-w Owners Manual - Page 114
Ev-ctoDEI, Derivative, Given, Point
 |
UPC - 079767128685
View all Casio CFX-9800G-w manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 114 highlights
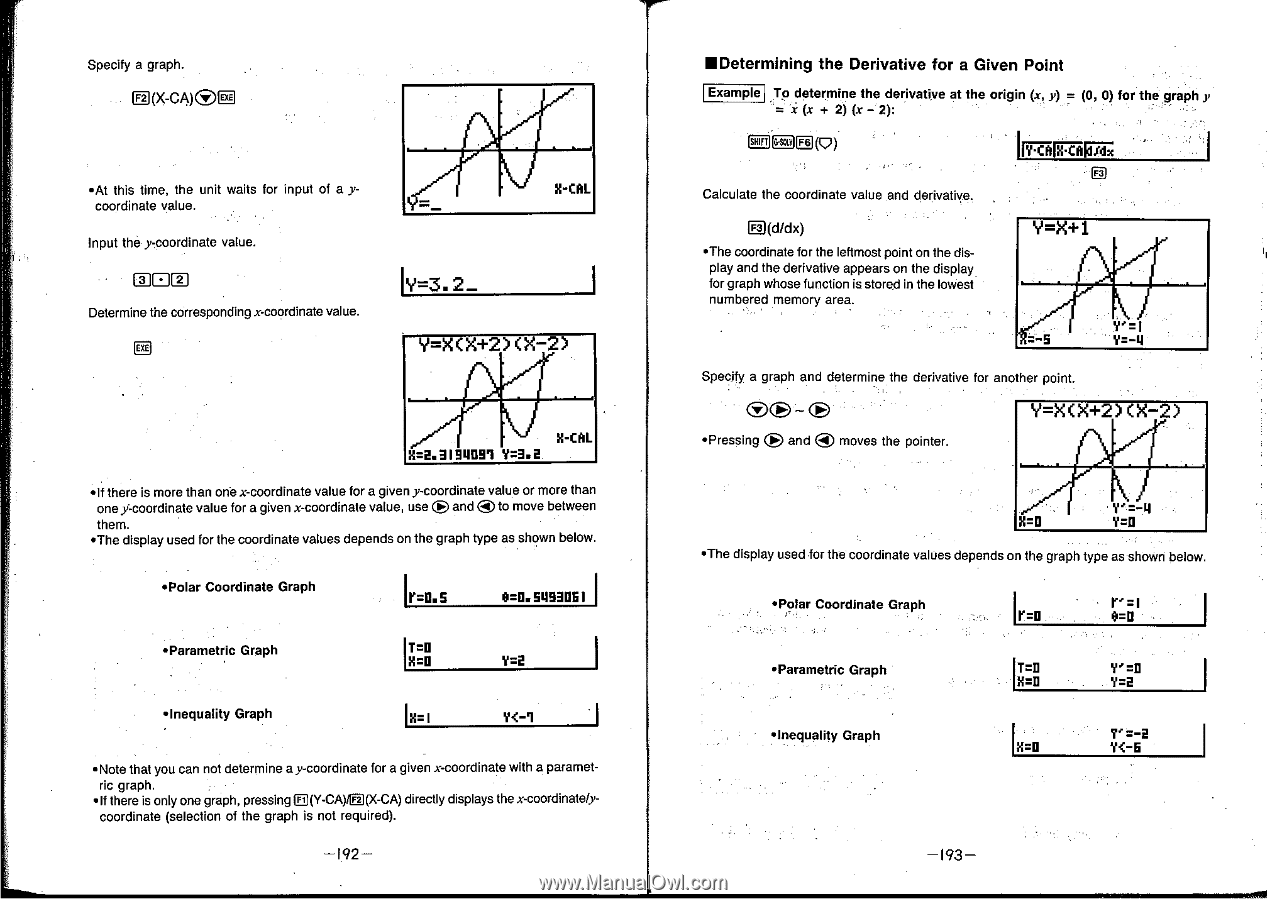
Specify a graph. Ev-cto(DEI •At this time, the unit waits for input of a ycoordinate value. X-CAL Input the y-coordinate value. LIM Determine the corresponding x-coordinate value. IY=3. 2_ Y=X(X+2) (X-2) ALX-CAL X=2.21911099 Y=2.2 •If there is more than one x-coordinate value for a give y-coordinate value or more than one y-coordinate value for a given x-coordinate value, use ® and ® to move between them. *The display used for the coordinate values depends o the graph type as shown below. *Polar Coordinate Graph lr=0.5 0=0.5493USI •Parametric Graph *Inequality Graph Y=2 IX= I Y
Specify
a
graph.
Ev-cto(DEI
•At
this
time,
the
unit
waits
for
input
of
a
y-
coordinate
value.
Input
the
y-coordinate
value.
LIM
Determine
the
corresponding
x-coordinate
value.
X
-CAL
IY=3.
2_
Y=X(X+2)
(X-2)
AL
X-CAL
X=2.219
1
1099
Y=2.2
•If
there
is
more
than
one
x-coordinate
value
for
a
give
y-coordinate
value
or
more
than
one
y-coordinate
value
for
a
given
x-coordinate
value,
use
®
and
®
to
move
between
them.
*The
display
used
for
the
coordinate
values
depends
o
the
graph
type
as
shown
below.
*Polar
Coordinate
Graph
•Parametric
Graph
*Inequality
Graph
lr=0.5
0=0.5493USI
Y=2
I
X=
I
Y<-1
•
Note
that
you
can
not
determine
ay
-coordinate
for
a
given
x-coordinate
with
a
paramet-
ric
graph.
•
If
there
is
only
one
graph,
pressing
0(Y-CA)0X-CA)
directly
displays
the
x-coordinate/y-
coordinate
(selection
of
the
graph
is
not
required).
•Determining
the
Derivative
for
a
Given
Point
To
determine
the
derivative
at
the
origin
(x,
=
(0,
0)
for
the
graph
y
x
(x
+
2)
(x
—
2):
Example
33
E(Q)
Calculate
the
coordinate
value
and
derivative.
D(d/dx)
*The
coordinate
for
the
leftmost
point
on
the
dis-
play
and
the
derivative
appears
on
the
display,
for
graph
whose
function
is
stored
in
the
lowest
numbered
memory
area.
PM
n.10
Y=X+1
=
I
Y=-
1
1
Specify
a
graph
and
determine
the
derivative
for
another
point.
•Pressing
®
and
®
moves
the
pointer.
Y=X(X+2)
(X-2)
X=0
Y'=-11
Y=1:1
•The
display
used
for
the
coordinate
values
depends
on
the
graph
type
as
shown
below.
•Polar
Coordinate
Graph
rri
r=o
oro
•
Parametric
Graph
IgE
,
y
1'
4
11
•
Ineguality
Graph
X=0
—192—
-193—