HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 2 - LAN Switching Command Refer - Page 21
display packet-drop, Syntax, Views, Predefined user roles, Parameters, Examples
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 21 highlights
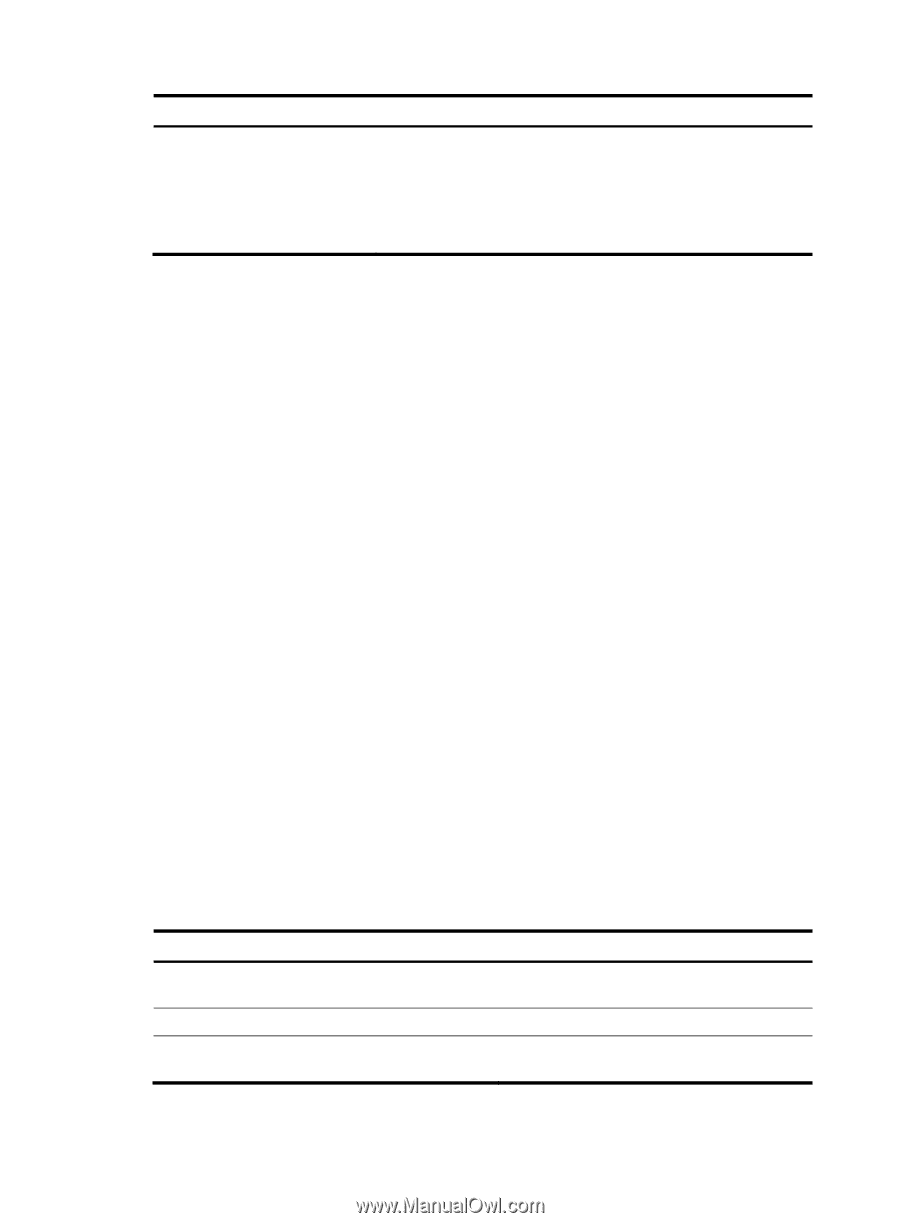
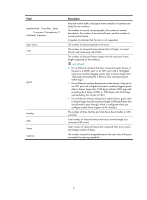
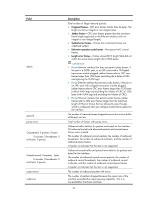
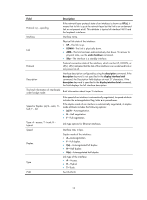
Field Cause Description Causes for the physical state of an interface to be DOWN. • Not connected-No physical connection exists (possibly because the network cable is disconnected or faulty). • Administratively DOWN-The port was shut down with the shutdown command. To restore the physical state of the interface, use the undo shutdown command. display packet-drop Use display packet-drop to display information about packets dropped on an interface or multiple interfaces. Syntax display packet-drop { interface [ interface-type [ interface-number ] ] | summary } Views Any view Predefined user roles network-admin network-operator Parameters interface-type: Specifies an interface type. If you do not specify an interface type, this command displays information about dropped packets on all the interfaces on the device. interface-number: Specifies an interface number. If you specify an interface type only, this command displays information about dropped packets on the specified type of interfaces. summary: Displays the summary of dropped packets on all interfaces. Examples # Display information about dropped packets on Ten-GigabitEthernet1/1/5. display packet-drop interface ten-gigabitethernet 1/1/5 Ten-GigabitEthernet1/1/5: Packets dropped due to full GBP or insufficient bandwidth: 0 Packets dropped due to Fast Filter Processor (FFP): 0 Packets dropped due to STP non-forwarding state: 0 Table 5 Command output Field Packets dropped due to full GBP or insufficient bandwidth Packets dropped due to Fast Filter Processor FFP Packets dropped due to STP non-forwarding state Description Packets that are dropped because the buffer is used up or the bandwidth is insufficient. Packets that are filtered out. Packets that are dropped because STP is in the non-forwarding state. 14