HP NetServer AA 4000 HP NetServer AA 6200 Solution Release 3.0 Administrator&a - Page 220
Isolating Faults, If you have local access to the server
 |
View all HP NetServer AA 4000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 220 highlights
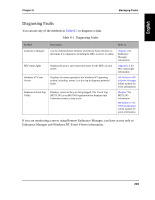
Chapter 8 Managing Faults Isolating Faults If you have local access to the server, check the following in the order that they are listed: Step 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Action Notes Check the upper and lower status lights on the handles of each of the four MICs in your server. If both sets of lights are solid green, the MICs are working properly and communicating correctly. If any of the lights are orange, red, off, there may be a problem with the MIC. Refer to Appendix A for a description of the MIC status lights. Using the Endurance Manager Administration Window, note any MIC port states that are listed as Failed, Lost Power, PCI Reset, Unknown/Unavailable, or Uninitialized. Refer to MIC Port State Display Lights in Chapter 2 for a description of the MIC port states. Using the Endurance Manager Administration Window and the Device Status Window, note any components that are not active, online, or standby. Check for and correct any obvious failures. For example, check for loose cables. If the CE is active, check the Windows NT Event Viewer for messages beginning with or . Reference those events (in the HP NetServer AA Solution Messages online manual) for information and corrective action. Because the IOPs may have slightly different error messages, depending on the state of the server, check the Windows NT Event Viewer for messages beginning with or . Reference those events (in the HP NetServer AA Solution Messages online manual) for information and corrective action. Review the IOP event logs for nonmessages that indicate a problem with an IOP-connected device. For example, check for messages logged by the SCSI adapter driver. 204