HP NetServer AA 4000 HP NetServer AA 6200 Solution Release 3.0 Administrator&a - Page 24
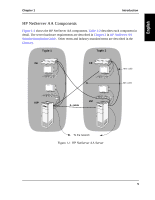
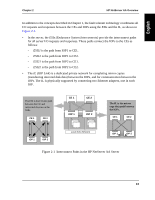
CE Compute Element, IOPs I/O Processors, MIC Marathon Interface Card, IL IOP Link cable
 |
View all HP NetServer AA 4000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 24 highlights
Chapter 1 Introduction Each system in the server (Figure 1-2) performs specific tasks, functioning as either a CE or IOP: • CE (Compute Element) contains the server CPU (s) and memory that supports the Windows NT operating system and applications. Because there are two CEs, the CEs provide the redundant CPU (s) and memory for the server. • IOPs (I/O Processors) contain the keyboard and mouse, mirrored SCSI devices, redundant network adapters, and other I/O devices. Because there are two IOPs, the mirrored SCSI devices (one on each IOP) provide fault tolerant data storage, and the redundant network adapters (one on each IOP) provide redundant network connectivity. The IOPs handle all server I/O requests. The server uses MICs and the ILs to interconnect four standard systems into the server configuration. This enables these systems to function as one server: • MIC (Marathon Interface Card) is an adapter that provides a high speed interconnect path for the server. There are four MICs in a server: one in each IOP, and one in each CE. • IL (IOP Link) cable connects IOP1 and IOP2. By using redundant hardware, HP is also able to implement SplitSite technology in your server. SplitSite enables you to locate each tuple of a server residing in different locations. This provides a method of offsite data protection while also providing protection from potential site disasters. 8