Cisco SA520-K9 Administration Guide - Page 39
Viewing the WAN Status, Configuring the Optional WAN, - problems
 |
UPC - 882658266744
View all Cisco SA520-K9 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 39 highlights
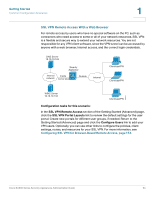
Networking Configuring the WAN Connection 2 • MTU Size: If you chose Customer for the MTU Type, enter the custom MTU size in bytes. The MTU (Maximum Transmit Unit) is the size of the largest packet that can be sent over the network. The standard MTU value for Ethernet networks is usually 1500 Bytes. For PPPoE connections, it is 1492 Bytes. Unless a change is required by your ISP, it is recommended that the MTU values be left as is. STEP 7 Click Apply to save your settings. NOTE Next steps: • If you are using the Getting Started (Basic) page, click Getting Started in the menu bar, and then continue with the list of configuration tasks. • To check the WAN status, click WAN > WAN Status. For more information, see Viewing the WAN Status, page 39. • If you need to create PPPoE profiles, click WAN > PPPoE Profiles. For more information, see Creating PPPoE Profiles, page 40. • If you need to configure another ISP link, click Optional Port > Optional Port Mode and choose WAN for the port mode. After saving your settings on that page, click Optional Port > WAN to configure the WAN connection. For more information, see Configuring the Optional WAN, page 54. • If you are having problems with your WAN connection, see the Internet Connection, page 217 in Appendix A, "Troubleshooting." Viewing the WAN Status You can check the WAN status, renew the connection, or release the connection. STEP 1 Click Networking >WAN > WAN Status. The WAN Status window opens. This page displays the following types of information about the dedicated WAN and the optional WAN (if applicable): • Connection Time • Connection Type: Dynamic IP (DHCP) or Static IP • Connection State: Connected or Disconnected • Link State: Up or Down Cisco SA500 Series Security Appliances Administration Guide 39