Cisco SA520-K9 Administration Guide - Page 67
DMZ DHCP Leased Clients, Routing
 |
UPC - 882658266744
View all Cisco SA520-K9 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 67 highlights
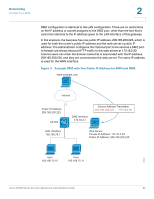
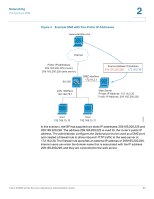
Networking Routing 2 DMZ DHCP Leased Clients This page displays a list of the DHCP-assigned IP addresses and hardware addresses of the DMZ clients. Click Networking > Optional Port > DMZ DHCP Clients. Routing If needed, you can change the routing mode, configure static routing, or configure dynamic routing on your security appliance. • Routing, page 67 • Static Routing, page 68 • Dynamic Routing, page 69 Routing Depending on the requirements of your ISP, you can configure the security appliance in NAT routing mode or Classic routing mode. By default, NAT is enabled. Network Address Transalation (NAT) is a technique that allows several computers on a LAN to share an Internet connection. The computers on the LAN use a private IP address range while the WAN port on the router is configured with a single public IP address. Along with connection sharing, NAT also hides internal IP addresses from the computers on the Internet. STEP 1 Click Networking > Routing > Routing. The Routing Mode window opens. STEP 2 Choose one of the following options: • NAT: Choose this option if your ISP has assigned only one IP address to you or if you are sharing IP addresses across several devices such as your LAN, and using the other dedicated devices for DMZ. NAT is the default option. • Classic Routing: Choose this option if your ISP has assigned an IP address for each of the computers that you use. Cisco SA500 Series Security Appliances Administration Guide 67