Cisco SA520-K9 Administration Guide - Page 63
Networking, Example DMZ with Two Public IP Addresses
 |
UPC - 882658266744
View all Cisco SA520-K9 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 63 highlights
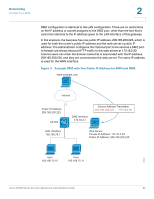
Networking Configuring a DMZ Figure 4 Example DMZ with Two Public IP Addresses www.example.com 2 Internet Public IP Addresses 209.165.200.225 (router) 209.165.200.226 (web server) SA 500 LAN Interface 192.168.75.1 DMZ interface 172.16.2.1 Source Address Translation 209.165.200.226 172.16.2.30 Web Server Private IP Address: 172.16.2.30 Public IP Address: 209.165.200.226 235610 User 192.168.75.10 User 192.168.75.11 In this scenario, the ISP has supplied two static IP addresses: 209.165.200.225 and 209.165.200.226. The address 209.165.200.225 is used for the router's public IP address. The administrator configures the Optional port to be used as a DMZ port and created a firewall rule to allow inbound HTTP traffic to the web server at 172.16.2.30. The firewall rule specifies an external IP address of 209.165.200.226. Internet users can enter the domain name that is associated with the IP address 209.165.200.226, and they are connected to the web server. Cisco SA500 Series Security Appliances Administration Guide 63