D-Link DGS-3200-10 Product Manual - Page 136
IP-MAC-Port Binding (IMPB), General Overview, Common IP Management Security Issues - cli manual
 |
UPC - 790069306310
View all D-Link DGS-3200-10 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 136 highlights
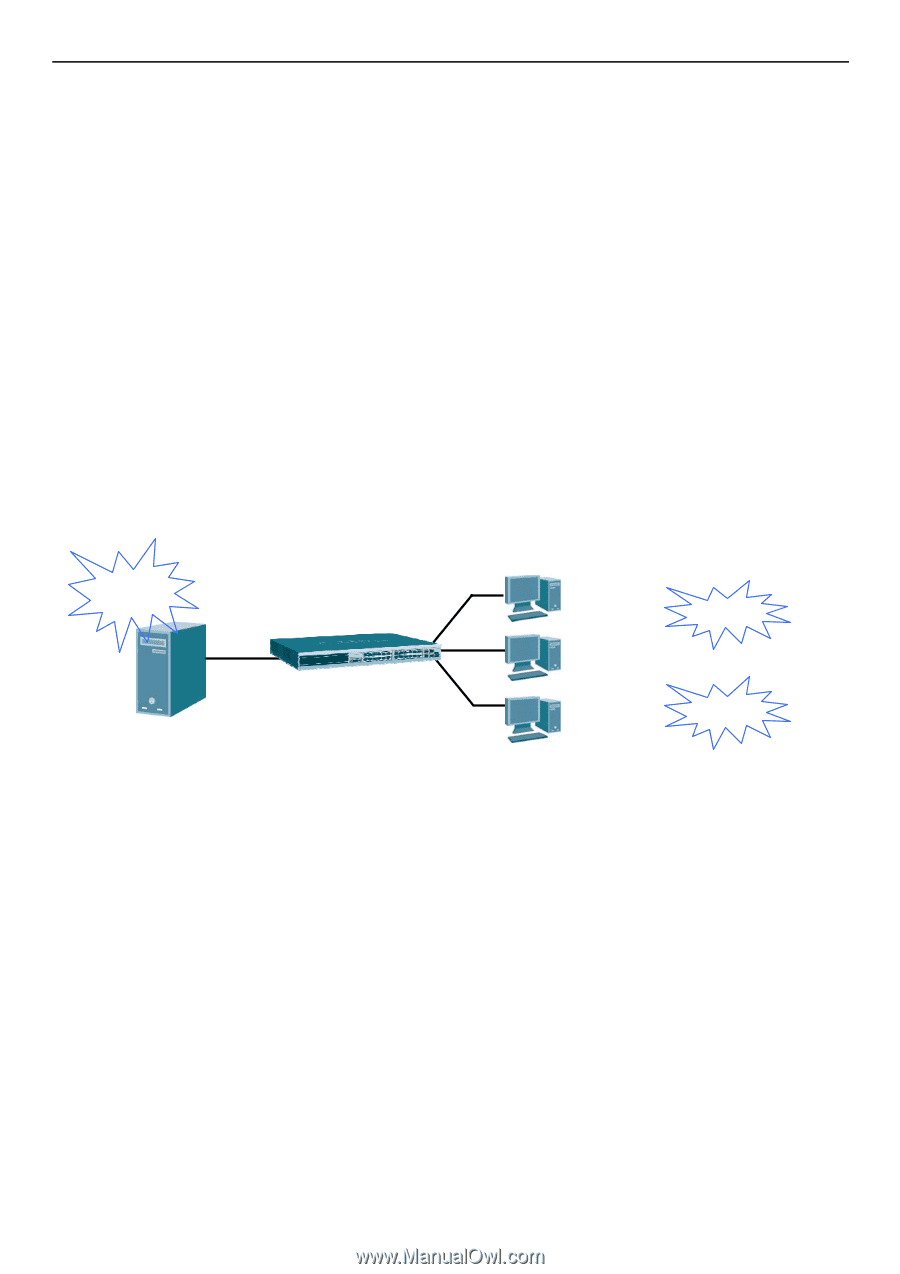
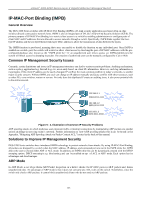
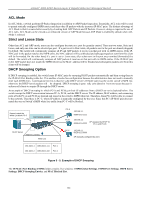
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Managed Switch IP-MAC-Port Binding (IMPB) General Overview The DGS-3200 Series switches offer IP-MAC-Port Binding (IMPB), a D-Link security application used most often on edge switches directly connected to network hosts. IMPB is also an integral part of D-Link's End-to-End Security Solution (E2ES). The primary purpose of IP-MAC-Port Binding is to restrict client access to a switch by enabling administrators to configure pairs of client MAC and IP addresses that are allowed to access networks through a switch. Specifically, IMPB binds together the fourbyte IP address and the six-byte Ethernet link layer MAC address to allow the transmission of data between the layers. The IMPB function is port-based, meaning that a use r can enable or disable the function on any individual port. Once IMPB is enabled on a switch port, the switch will restrict or allow client access by chec king the pair of IP-MAC addresses with the preconfigured database, also known as the "I MPB white lis t". If an unauthorized user tries to access a n IMPB-enabled port, the system will block access by dropping its packet. The creation of authorized users can be manually configured by CLI or Web. Common IP Management Security Issues Currently, certain limitations and issues in IP management structures can lead to serious security problems. Auditing mechanisms, such as syslo g, app lication lo g, firewall lo g, et c, are m ainly based on c lient IP i nformation. However, s uch l og i nformation i s meaningless if the client IP address can be easily changed. IP conflict, the most common problem in today's networks, is another major security concern. Without IMPB, any user can change an IP address manually and cause conflict with other resources, such as other PCs, core switches, routers or servers. Not only does this duplicate IP create an auditing issue, it also poses potential risk to the entire network. Auditing Problem 192.168.1.1 00E0-0211-1111 192.168.1.2 00E0-0211-2222 192.168.1.3 00E0-0211-3333 IP Conflict IP Conflict Figure 5 - 4. Illustration of Common IP Security Problems ARP spoofing attacks in which malicious users intercept traffic or interrupt connections by manipulating ARP packets are another serious ch allenge in secu ring t oday's network. Further information on how A RP sp oofing attacks wor k can be fo und i n t he Appendix, "Mitigating ARP Spoofing Attack via Packet Content ACL," located in the back of this manual. Solutions to Improve IP Management Security DGS-3200 Series switches have introduced IMPB technology to protect networks from attacks. By using IP-MAC-Port Binding, all packets are dropped by a switch when the MAC address, IP address, and connected port are not in the IMPB white list. IMPB allows the user to choose either ARP or ACL mode. In addition, an IMPB white list can be dynamically created with the DHCP snooping option. DHCP snoo ping is a g lobal settin g and can be en abled on top of ACL or AR P mode. Each option has it s advantages and disadvantages. ARP Mode In ARP M ode, a swi tch pe rforms AR P Packet In spection i n w hich i t checks t he IP -MAC pai rs i n AR P packets and denies unauthorized ones. An advantage of ARP mode is that it does not consume any ACL ru les on the switch. Nonetheless, since the switch only checks ARP packets, it cannot block unauthorized clients who do not send out ARP packets. 123