D-Link DGS-3200-10 Product Manual - Page 52
SNMP Settings, Traps, MIBs - des e
 |
UPC - 790069306310
View all D-Link DGS-3200-10 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 52 highlights
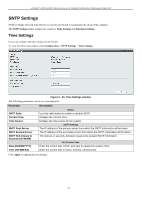
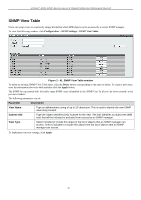
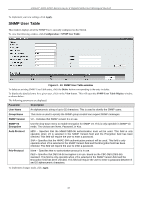
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Managed Switch SNMP Settings Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI Layer 7 (Application Layer) designed specifically for managing and monitoring network devices. SNMP enables network management stations to read and modify the settings of gateways, routers, switches, a nd other net work devices. Use SNMP t o co nfigure sy stem f eatures for proper operation, monitor pe rformance an d detect potential problems in the Switch, switch group or network. Managed devices that support SNMP include software (referred to as an agent), which runs locally on the device. A defined set of variables (m anaged objects) i s m aintained b y t he S NMP a gent an d used to m anage t he de vice. These o bjects are defined i n a Management I nformation B ase (M IB), which provides a standard presentation o f t he information c ontrolled by t he o n-board SNMP agent. SNMP defines both the format of t he MIB specifications and the protocol used to access this information over the network. The Switch supports the SNMP versions 1, 2c, and 3. The three versions of SNMP vary in the level of security provided between the management station and the network device. In SNMP v.1 and v.2, user authentication is accomplished using 'community strings', which function like passwords. The remote user SNMP application and the Switch SNMP must use the same community string. SNMP packets from any station that has not been authenticated are ignored (dropped). The default community strings for the Switch used for SNMP v.1 and v.2 management access are: public - Allows authorized management stations to retrieve MIB objects. private - Allows authorized management stations to retrieve and modify MIB objects. SNMPv3 uses a more sophisticated authentication process that is sep arated into two parts. The first p art is to maintain a list of users and their attributes that are allowed to act as SNMP managers. The second part describes what each user on that list can do as an SNMP manager. The Switch allows groups of users to be listed and configured with a shared set of privileges. The SNMP version may also be set for a l isted group of S NMP m anagers. T hus, y ou m ay creat e a group of S NMP m anagers t hat a re allowed t o vi ew read-only information or receive traps using SNMPv1 while assigning a higher level of secu rity to another group, granting read/write privileges using SNMPv3. Using S NMPv3 i ndividual users or g roups of S NMP m anagers ca n be al lowed t o p erform or be restricted f rom pe rforming specific SNM P m anagement fun ctions. Th e fun ctions allowed or re stricted are defined usin g th e Obj ect Id entifier (OID) associated wit h a s pecific MIB. An a dditional layer of secu rity is av ailable for SNMPv3 in th at SNMP m essages m ay b e encrypted. To read more about how to configure SNMPv3 settings for the Switch read the next section. Traps Traps are m essages that alert network personnel of eve nts that occur on the Switch. The eve nts ca n be as se rious as a reboot (someone acci dentally turned OFF the Switch), or less serious like a port status ch ange. The Switch generates tra ps and se nds them to the trap recipient (or network manager). Typical traps include trap messages for Authentication Failure, Topology Change and Broadcast\Multicast Storm. MIBs The S witch i n t he M anagement In formation B ase (MIB) st ores m anagement and counter i nformation. The Switch u ses t he standard MIB-II Management Information Base module. Consequently, values for MIB objects can be retrieved from any SNMPbased network management software. In addition to the standard MIB-II, the Switch also supports its own proprietary enterprise MIB as an extended Management Information Base. Specifying the MIB Object Identifier may also retrieve the proprietary MIB. MIB values can be either read-only or read-write. The Switch incorporates a flexible SNMP management for the switching environment. SNMP management can be customized to suit the needs of the networks and the preferences of the network administrator. Use the SNMP V3 menus to select th e SNMP version used for specific tasks. The Switch supports the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) versions 1, 2c, and 3. The administrator can specify the SNMP version use d t o m onitor a nd c ontrol t he S witch. The t hree ve rsions o f S NMP va ry i n t he level o f sec urity pro vided between the management station and the network device. SNMP settings are configured using the menus located on the SNMP V3 folder of the Web manager. Workstations on the network that are allowed SNMP privileged access to the Switch can be restricted with the Management Station IP Address menu. 39