D-Link DGS-3200-10 Product Manual - Page 80
Port-based VLANs, VLAN Segmentation, VLAN and Trunk Groups, VLAN Name, Switch Ports
 |
UPC - 790069306310
View all D-Link DGS-3200-10 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 80 highlights
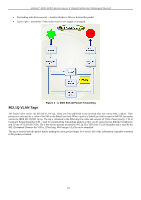
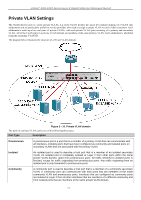
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Managed Switch An example is presented below: VLAN Name VID System (default) 1 Engineering 2 Sales 5 Switch Ports 5, 6, 7 9, 10 1, 2, 3, 4 Port-based VLANs Table 3 - 1. VLAN Example - Assigned Ports Port-based VLANs limit traffic th at flows into and out of switch ports. Thus, all devices connected to a port are m embers of th e VLAN(s) the port belongs to, whether there is a single computer directly connected to a switch, or an entire department. On port-based VL ANs, NIC s do not nee d to be a ble to i dentify 802.1Q tags i n pac ket heade rs. NICs send and receive normal Ethernet packets. If the packet's destination lies on the same segment, communications take place using normal Ethernet protocols. Even though this is always the case, when the destination for a packet lies on another switch port, VLAN considerations come into play to decide if the packet gets dropped by the Switch or delivered. VLAN Segmentation Take for exam ple a pac ket that is transm itted by a m achine on Port 1 t hat is a member of VLAN 2. If t he d estination lies o n another port (found through a normal forwarding table lookup), the Switch then looks to see if the other port (Port 10) is a member of VLAN 2 (and can therefore receive VLAN 2 packets). If Port 10 is not a member of VLAN 2, then the packet will be dropped by the Switch and will not reach its d estination. If Port 10 is a member of VLAN 2, the packet will g o through. This selective forwarding feature based on VLAN criteria is h ow VLANs segment networks. The key point being that Port 1 will only transmit on VLAN 2. VLAN and Trunk Groups The members of a trunk grou p have the same V LAN setting. Any VLAN setting on the m embers of a trunk group will apply to the other member ports. NOTE: In order to use VLAN segmentation in conjunction with port trunk groups, first set the port trunk group(s), and then configure the VLAN settings. To change the port trunk grouping with VLANs already in place it is unnecessary to reconfigure the VLAN settings after changing the port trunk group settings. VLAN settings will automatically change in conjunction with the change of the port trunk group settings. 67