Dell PowerConnect W Clearpass 100 Software 3.7 Deployment Guide - Page 360
Updating Plugins, Destroying a Cluster, Cluster Troubleshooting, Show details, Local, Status
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect W Clearpass 100 Software manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 360 highlights
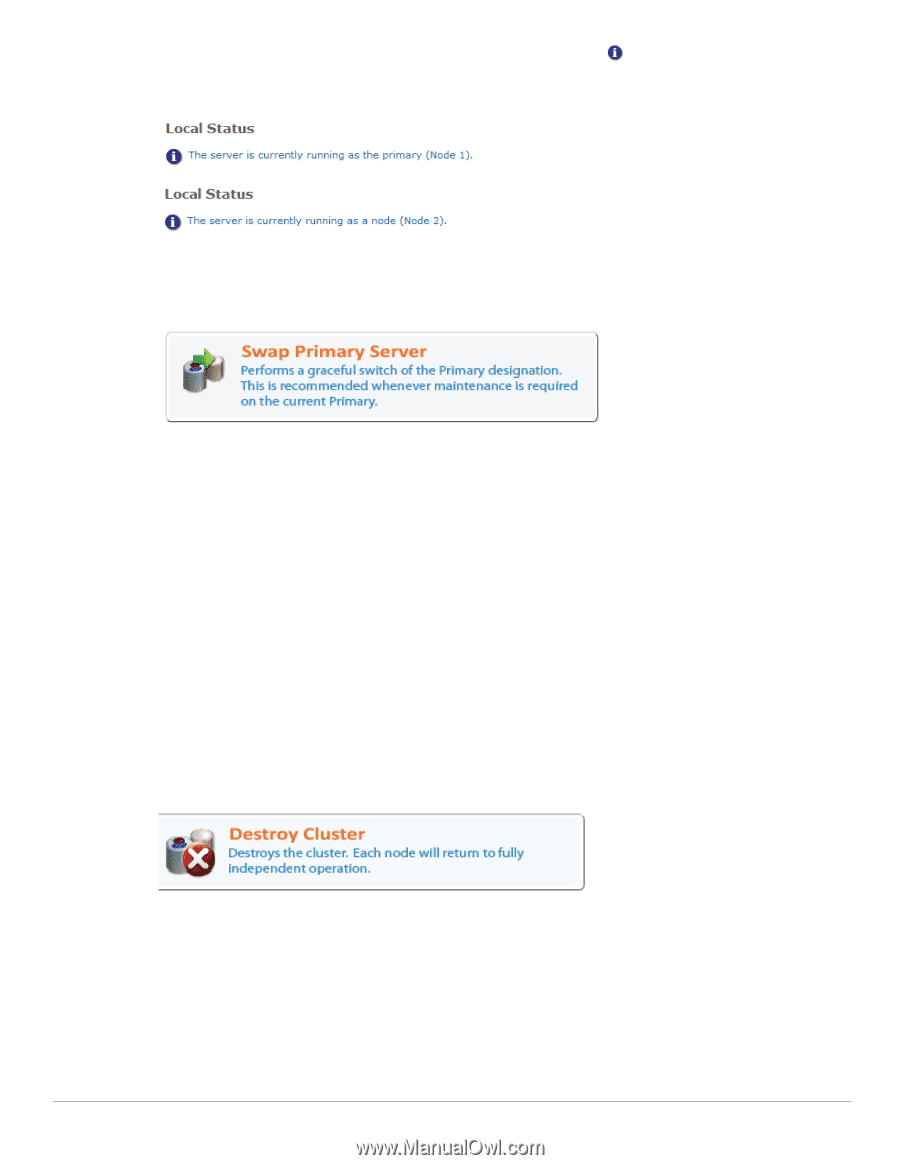
To check the current status of a node, log into that node and click the Show details link displayed with the cluster status on the High Availability page. The node's current status is displayed under the Local Status heading. Use this procedure to make the current primary node the secondary node: 1. Log into the current secondary node of the cluster. 2. Click Cluster Maintenance, and then click the Swap Primary Server command link. 3. A progress meter is displayed while the primary node is switched. The cluster's virtual IP address will be temporarily unavailable while the swap takes place. 4. The swap is complete. The secondary node is now the new primary node for the cluster. The cluster is back in a fault-tolerant mode of operation. 5. Perform any required maintenance on the new secondary node. Updating Plugins Plugins cannot be updated while High Availability is running. Because exact synchronization of the two servers is required for High Availability Services, you must first destroy the cluster, then re-create the cluster after the plugins are updated. See Destroying a Cluster and Cluster Setup in this chapter. For information on updating plugins, see Plugin Manager in the Administrator Tasks chapter. Destroying a Cluster The Destroy Cluster command link is used to shut down a cluster and return to independent nodes. Avoid using this command when you are accessing the cluster using its virtual IP address, as the virtual IP address will no longer be available when the cluster has been destroyed. Immediately after the cluster is destroyed, both nodes will have the same database and configuration state. However, changes on one node will no longer be replicated to the other node as the cluster is no longer functioning. Cluster Troubleshooting When building a cluster, use the recommended values for the downtime threshold, keep-alive rate and configuration sync rate. You should only change these values if you have a specific requirement and have verified that different values can be used to meet that requirement. 360 | High Availability Services Amigopod 3.7 | Deployment Guide