D-Link DES-3528 Product Manual - Page 117
MLD Snooping Settings, MLD Control Messages, Data Driven Learning
 |
UPC - 790069314346
View all D-Link DES-3528 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 117 highlights
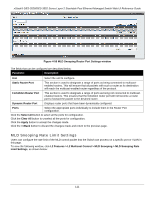
xStack® DES-3528/DES-3552 Series Layer 2 Stackable Fast Ethernet Managed Switch Web UI Reference Guide multicast group address, and then considers this port to be an active listening port. The active listening ports are the only ones to receive multicast group data. MLD Control Messages Three types of messages are transferred between devices using MLD snooping. These three messages are all defined by four ICMPv6 packet headers, labeled 130, 131, 132, and 143. 1. Multicast Listener Query - Similar to the IGMPv2 Host Membership Query for IPv4, and labeled as 130 in the ICMPv6 packet header, this message is sent by the router to ask if any link is requesting multicast data. There are two types of MLD query messages emitted by the router. The General Query is used to advertise all multicast addresses that are ready to send multicast data to all listening ports, and the Multicast Specific query, which advertises a specific multicast address that is also ready. These two types of messages are distinguished by a multicast destination address located in the IPv6 header and a multicast address in the Multicast Listener Query Message. 2. Multicast Listener Report, Version 1 - Comparable to the Host Membership Report in IGMPv2, and labeled as 131 in the ICMP packet header, this message is sent by the listening port to the Switch stating that it is interested in receiving multicast data from a multicast address in response to the Multicast Listener Query message. 3. Multicast Listener Done - Akin to the Leave Group Message in IGMPv2, and labeled as 132 in the ICMPv6 packet header, this message is sent by the multicast listening port stating that it is no longer interested in receiving multicast data from a specific multicast group address, therefore stating that it is "done" with the multicast data from this address. Once this message is received by the Switch, it will no longer forward multicast traffic from a specific multicast group address to this listening port. 4. Multicast Listener Report, Version 2 - Comparable to the Host Membership Report in IGMPv3, and labeled as 143 in the ICMP packet header, this message is sent by the listening port to the Switch stating that it is interested in receiving multicast data from a multicast address in response to the Multicast Listener Query message. Data Driven Learning The Switch allows you to implement data driven learning for MLD snooping groups. If data-driven learning, also known as dynamic IP multicast learning, is enabled for a VLAN, when the Switch receives IP multicast traffic on the VLAN, an MLD snooping group is created. Learning of an entry is not activated by MLD membership registration, but activated by the traffic. For an ordinary MLD snooping entry, the MLD protocol will take care of the aging out of the entry. For a data-driven entry, the entry can be specified not to age out or to age out by a timer. When the data driven learning State is enabled, the multicast filtering mode for all ports is ignored. This means multicast packets will be forwarded to router ports. NOTE: If a data-driven group is created and MLD member ports are learned later, the entry will become an ordinary MLD snooping entry. In other words, the aging out mechanism will follow the conditions of an ordinary MLD snooping entry. Data driven learning is useful on a network which has video cameras connected to a Layer 2 switch that is recording and sending IP multicast data. The Switch needs to forward IP data to a data centre without dropping or flooding any packets. Since video cameras do not have the capability to run MLD protocols, the IP multicast data will be dropped with the original MLD snooping function. MLD Snooping Settings Users can configure the settings for MLD snooping. To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Settings, as shown below: 108