D-Link DES-3528 Product Manual - Page 350
How ARP Spoofing Attacks a Network
 |
UPC - 790069314346
View all D-Link DES-3528 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 350 highlights
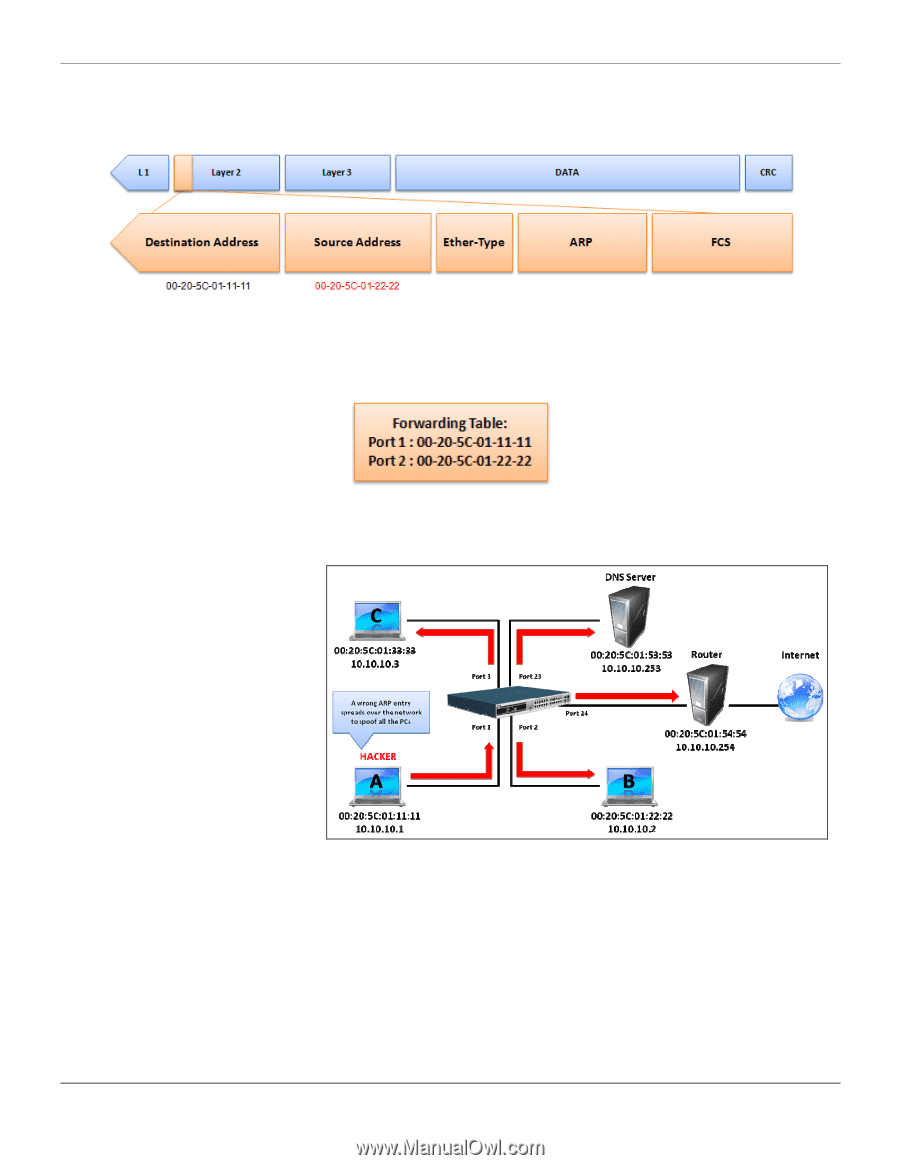
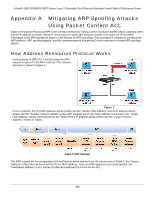
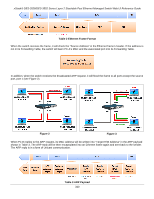
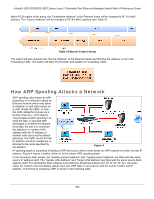
xStack® DES-3528/DES-3552 Series Layer 2 Stackable Fast Ethernet Managed Switch Web UI Reference Guide When PC B replies to the query, the "Destination Address" in the Ethernet frame will be changed to PC A's MAC address. The "Source Address" will be changed to PC B's MAC address (see Table 4). Table 4 Ethernet Frame Format The switch will also examine the "Source Address" of the Ethernet frame and find that the address is not in the Forwarding Table. The switch will learn PC B's MAC and update its Forwarding Table. How ARP Spoofing Attacks a Network ARP spoofing, also known as ARP poisoning, is a method to attack an Ethernet network which may allow an attacker to sniff data frames on a LAN, modify the traffic, or stop the traffic altogether (known as a Denial of Service - DoS attack). The principle of ARP spoofing is to send the fake, or spoofed ARP messages to an Ethernet network. Generally, the aim is to associate the attacker's or random MAC address with the IP address of another node (such as the default gateway). Any traffic meant for that IP address would be mistakenly redirected to the node specified by the attacker. Figure 4 IP spoofing attack is caused by Gratuitous ARP that occurs when a host sends an ARP request to resolve its own IP address. Figure-4 shows a hacker within a LAN to initiate ARP spoofing attack. In the Gratuitous ARP packet, the "Sender protocol address" and "Target protocol address" are filled with the same source IP address itself. The "Sender H/W Address" and "Target H/W address" are filled with the same source MAC address itself. The destination MAC address is the Ethernet broadcast address (FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF). All nodes within the network will immediately update their own ARP table in accordance with the sender's MAC and IP address. The format of Gratuitous ARP is shown in the following table. 341