D-Link DES-3528 Product Manual - Page 367
VLT - Virtual LAN Trunk, SLIP - Serial Line Internet
 |
UPC - 790069314346
View all D-Link DES-3528 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 367 highlights
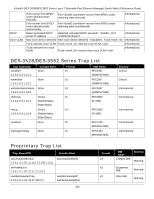
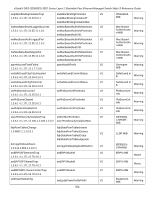
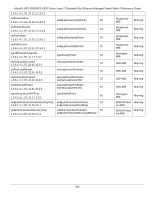
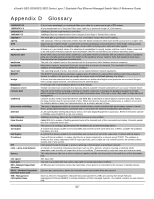
xStack® DES-3528/DES-3552 Series Layer 2 Stackable Fast Ethernet Managed Switch Web UI Reference Guide multicast protocol resilient link RJ-45 RMON RPS - Redundant Power System server farm SLIP - Serial Line Internet Protocol SNMP - Simple Network Management Protocol Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) standby port switch TCP/IP telnet TFTP - Trivial File Transfer Protocol UDP - User Datagram Protocol VLAN - Virtual LAN VLT - Virtual LAN Trunk VT100 Single packets copied to a specific subset of network addresses. These addresses are specified in the destinationaddress field of the packet. A set of rules for communication between devices on a network. The rules dictate format, timing, sequencing and error control. A pair of ports that can be configured so that one will take over data transmission should the other fail. See also main port and standby port. Standard 8-wire connectors for IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T networks. Remote Monitoring. A subset of SNMP MIB II that allows monitoring and management capabilities by addressing up to ten different groups of information. A device that provides a backup source of power when connected to the Switch. A cluster of servers in a centralized location serving a large user population. A protocol which allows IP to run over a serial line connection. A protocol originally designed to be used in managing TCP/IP internets. SNMP is presently implemented on a wide range of computers and networking equipment and may be used to manage many aspects of network and end station operation. A bridge-based system for providing fault tolerance on networks. STP works by allowing the user to implement parallel paths for network traffic, and ensure that redundant paths are disabled when the main paths are operational and enabled if the main paths fail. The port in a resilient link that will take over data transmission if the main port in the link fails. A device which filters, forwards and floods packets based on the packet's destination address. The switch learns the addresses associated with each switch port and builds tables based on this information to be used for the switching decision. A layered set of communications protocols providing Telnet terminal emulation, FTP file transfer, and other services for communication among a wide range of computer equipment. A TCP/IP application protocol that provides virtual terminal service, letting a user log in to another computer system and access a host as if the user were connected directly to the host. Allows the user to transfer files (such as software upgrades) from a remote device using your switch's local management capabilities. An Internet standard protocol that allows an application program on one device to send a datagram to an application program on another device. A group of location and topology-independent devices that communicate as if they are on a common physical LAN. A Switch-to-Switch link which carries traffic for all the VLANs on each Switch. A type of terminal that uses ASCII characters. VT100 screens have a text-based appearance. 358