D-Link DGS-6600-48TS Configuration Guide - Page 458
DHCP Server Screening, Overview, An introduction to DHCP Server Screening Configuration
 |
View all D-Link DGS-6600-48TS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 458 highlights
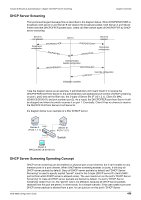
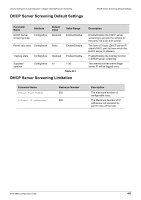
Volume 8-Security & Authentication / Chapter 43-DHCP Server Screening Chapter Overview Chapter 43 DHCP Server Screening Chapter Overview The following topics are included in this chapter, please go to the topic for more detailed information: • Chapter Overview • An introduction to DHCP Server Screening Configuration • DHCP Server Screening • DHCP Server Screening Operating Concept • Configuring DHCP Server Screening/Client Filtering • DHCP Server Screening/Client Filtering Configuration Commands • Configuring ip dhcp screening ports • Configuring ip dhcp screening suppress-time • Configuring ip dhcp screening • Enable DHCP Server screening function on ports • Add "permit" rule to DHCP server screening • Configuring ip dhcp screening trap-log • DHCP Server Screening Default Settings • DHCP Server Screening Limitation An introduction to DHCP Server Screening Configuration The following chapter discusses the different commands available for use in using and configuring DHCP Server screening and Snooping commands. The DHCP protocol is widely used to dynamically allocate the recycled network resources, for example, IP address. The DHCP Client sends a DHCP DISCOVER broadcast packet to the DHCP Server. The Client will send the DHCP DISCOVER again if it does not receive a response from the server within a specified time. After the DHCP Server receives the DHCP DISCOVER packet, it allocates resources to the Client, for example, IP address according to the appropriate policy, and sends the DHCP OFFER packet. After receiving the DHCP OFFER packet, the DHCP Client sends a DHCP REQUEST packet to obtain the server lease. After receiving the DHCP REQUEST packet, the server verifies whether the resources are available. If so, it sends a DHCP ACK packet. If not, it sends a DHCP NAK packet. Upon receiving the DHCP ACK packet, the DHCP Client starts to use the resources assigned by the server in condition that the ARP verification resources are available. If it receives the DHCP NAK packet, the DHCP Client will send the DHCP DISCOVER packet again. DHCP Snooping TRUST port: Because the packets for obtaining IP addresses through DHCP are in the form of broadcast, some illegal servers may prevent users from obtaining IP addresses, or even cheat and steal user information. To solve this problem, DHCP Snooping classifies the ports into two types: TRUST port and UNTRUST port. The device forwards only the DHCP reply packets received through the TRUST port while discarding all the DHCP reply packets from the UNTRUST port. In this way, the illegal DHCP Server can be shielded by setting the port connected to the legal DHCP Server as a TRUST port and other ports as UNTRUST ports. DHCP Snooping binding database: By snooping the packets between the DHCP Clients and the DHCP Server, DHCP Snooping combines the IP address, MAC address, VID, port and lease time into a entry to form a DHCP Snooping user database. DGS-6600 Configuration Guide 458