HP MSA 1040 HP MSA 1040 SMU Reference Guide (762784-001, March 2014) - Page 125
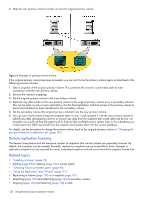
Remote replication disaster recovery, replication processing until controller recovery occurs.
 |
View all HP MSA 1040 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 125 highlights
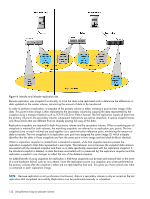
• The reserve size is calculated as follows: • If the primary volume and the snap pool are each less than 500 GB, the reserve will be the same size as the primary volume. • If the primary volume is larger than 500 GB, the reserve size will be the maximum, 500 GB. • If the snap pool is larger than 500 GB, the reserve will be the same size as the snap pool. • The required space in the vdisk is calculated as follows: • If the combined size of the primary volume and the reserve is less than the combined size of the primary volume and the snap pool, the required space is the combined size of the primary volume and the snap pool. • If the combined size of the primary volume and the reserve is larger than the combined size of the primary volume and the snap pool, the required space is the combined size of the primary volume and the reserve. The following table shows examples of how much available space a vdisk must have in order to be shown by the vdisk option. If you want to replicate a volume whose size is not shown, you can use the above calculations to determine how much available space the secondary vdisk must have. Table 11 Available space required for a vdisk to be selectable to contain a secondary volume Primary volume Available space Primary volume Available space Primary volume Available space size (GB) required in size (GB) required in size (GB) required in vdisk (GB) vdisk (GB) vdisk (GB) 100 200 1100 1600 2100 2600 200 400 1200 1700 2200 2700 300 600 1300 1800 2300 2800 400 800 1400 1900 2400 2900 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 600 1100 1600 2100 2600 3120 700 1200 1700 2200 2700 3240 800 1300 1800 2300 2800 3360 900 1400 1900 2400 2900 3480 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3600 Remote replication disaster recovery Replication can continue in the event of system faults such as: • Temporary communication failure. Remote replication will retry replication operations according to user-configured policies. • Controller failure. In a dual-controller system, failover will occur and the surviving controller will take over replication processing until controller recovery occurs. • Disk or power supply failure. If a disaster causes the primary volume to become inaccessible, you can set the secondary volume to be the primary volume so that volume can be mapped to hosts. Disaster recovery requires user intervention because decisions must be made based on the data content of replication volumes and their snapshots. 1. Synchronize the secondary volume to a replication snapshot, preferably a replication sync point. Any data written to the primary volume since the last-completed replication will not be available. 2. After synchronization, set the secondary volume to be the new primary volume. About the Remote Snap replication feature 125